Malignant Otitis Externa (MOE)/Skull base osteomyelitis
Introduction
Malignant otitis externa (MOE), also known as necrotizing otitis externa, is a rare and severe infection of the external ear canal. It is typically caused by the bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa. MOE primarily affects individuals with compromised immune systems, such as the elderly or those with diabetes. The infection starts in the ear canal and can spread to surrounding tissues, including the skull base.
The clinical presentation of MOE is characterized by severe ear pain, foul-smelling discharge, hearing loss, and swelling in the affected area. Left untreated, MOE can lead to serious complications, such as bone erosion, cranial nerve involvement, and even spread to nearby structures like the brain.
MRI plays a crucial role in diagnosing and staging MOE. On MRI, findings consistent with MOE include soft tissue inflammation and edema in the external ear canal, extending to the adjacent temporal bone and skull base. The involved structures may demonstrate enhancement following the administration of contrast material. MRI can also help identify complications such as abscess formation, osteomyelitis, and involvement of the cranial nerves or nearby blood vessels.
Additionally, MRI can aid in monitoring the response to treatment and assessing disease progression. It provides detailed anatomical information and helps guide clinicians in determining the extent of the infection, planning surgical interventions if necessary, and evaluating the overall response to therapy.

Indications for MOE/Skull base MRI scan
- Malignant otitis externa (MOE)
- Skull base osteomyelitis
Contraindications
- Any electrically, magnetically or mechanically activated implant (e.g. cardiac pacemaker, insulin pump biostimulator, neurostimulator, cochlear implant, and hearing aids)
- Intracranial aneurysm clips (unless made of titanium)
- Pregnancy (risk vs benefit ratio to be assessed)
- Ferromagnetic surgical clips or staples
- Metallic foreign body in the eye
- Metal shrapnel or bullet
Patient preparation MOE/Skull base MRI scan
- A satisfactory written consent form must be taken from the patient before entering the scanner room
- Ask the patient to remove all metal objects including keys, coins, wallet, cards with magnetic strips, jewellery, hearing aid and hairpins
- If possible provide a chaperone for claustrophobic patients (e.g. relative or staff )
- Offer earplugs or headphones, possibly with music for extra comfort
- Explain the procedure to the patient
- Instruct the patient to keep still
- Note the hight and weight of the patient
Positioning for MOE/Skull base MRI scan
- Head first supine
- Position the head in the head coil and immobilise with cushions
- Give cushions under the legs for extra comfort
- Centre the laser beam localiser over the nose tip
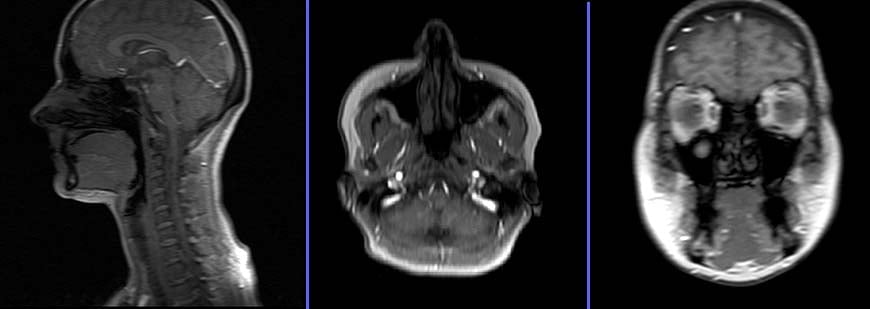
MRI Malignant Otitis Externa (MOE) protocols and planning
MOE/Skull base MRI scan localiser
A three-plane localizer must be taken at the beginning to localize and plan the sequences. Localizers are usually less than 25 seconds and are T1-weighted low-resolution scans.
T2 stir axial 3mm SFOV
Plan the axial slices on the coronal plane and angle the planning block parallel to the right and left internal auditory meatus. Check the planning block in the other two planes. An appropriate angle must be given in the sagittal plane, parallel to the hard palate. The slices must sufficiently cover the skull base and should extend from the glabella down to the upper lip.

Parameters
TR 4000-5000 | TE 110 | FLIP 150 | NEX 3 | SLICE 3 MM | MATRIX 256X256 | FOV 180-200 | PHASE R>L | GAP 10% | TI 150 |
T1 tse axial 3mm SFOV
Plan the axial slices on the coronal plane and angle the planning block parallel to the right and left internal auditory meatus. Check the planning block in the other two planes. An appropriate angle must be given in the sagittal plane, parallel to the hard palate. The slices must sufficiently cover the skull base and should extend from the glabella down to the upper lip.

Parameters
TR 400-600 | TE 15-25 | SLICE 3 MM | FLIP 140 | PHASE R>L | MATRIX 256X256 | FOV 180-200 | GAP 10% | NEX(AVRAGE) 2 |
RESOLVE DWI axial 3mm
Plan the axial slices on the coronal plane and angle the planning block parallel to the right and left internal auditory meatus. Check the planning block in the other two planes. An appropriate angle must be given in the sagittal plane, parallel to the hard palate. The slices must sufficiently cover the skull base and should extend from the glabella down to the upper lip.

Parameters
TR 7000-9000 | TE 70 | FLIP 130 | NXA 1 2 | SLICE 3MM | MATRIX 192X192 | FOV 200-230 | PHASE R>L | GAP 10% | B VALUE 0 |
T2 STIR coronal 3mm SFOV
Plan the coronal slices on the axial plane and angle the planning block parallel to the right and left internal auditory meatus. Check the planning block in the other two planes. An appropriate angle must be given in the sagittal plane, perpendicular to the hard palate. The slices should be sufficient to cover the skull base from the zygomatic arch to the posterior border of the temporal bone.

Parameters
TR 4000-5000 | TE 110 | FLIP 150 | NEX 3 | SLICE 3 MM | MATRIX 256X256 | FOV 160-180 | PHASE R>L | GAP 10% | TI 150 |
T1 tse coronal 3mm small FOV
Plan the coronal slices on the axial plane and angle the planning block parallel to the right and left internal auditory meatus. Check the planning block in the other two planes. An appropriate angle must be given in the sagittal plane, perpendicular to the hard palate. The slices should be sufficient to cover the skull base from the zygomatic arch to the posterior border of the temporal bone.

Parameters
TR 400-600 | TE 15-25 | SLICE 3 MM | FLIP 140 | PHASE R>L | MATRIX 256X256 | FOV 170-180 | GAP 10% | NEX(AVRAGE) 2 |
MRV skull base 3D phase-contrast (PC) sagittal
Plan the sagittal 3D block on the axial plane and position the block parallel to the midline of the brain. Verify the planning block in the coronal plane, ensuring it is parallel to the line along the midline and 3rd ventricle. Place the saturation band at the bottom of the block in the sagittal planes to avoid capturing arterial signals. Ensure that the number of slices is sufficient to cover the entire brain from one temporal lobe to the other.
MRV of the brain is an important sequence in the MOE protocol because the infection can cause jugular vein and cavernous sinus thrombosis. If phase-contrast scanning is not available, dynamic contrast-enhanced venography of the skull base should be performed.

Parameters
TR 68-75 | TE 8-9 | FLIP 15 | NEX 2 | SLICE 1MM | MATRIX 256X256 | FOV 280 | PHASE A>P | GAP 20% | velocity 10 |
For contrast enhanced scans
Optional Scans
T1 VIBE DIXON 3D axial .7 mm isotropic SFOV post contrast
Plan the axial slices on the sagittal plane and angle the planning block parallel to the hard palate. Check the planning block in the other two planes. An appropriate angle must be provided in the coronal plane, perpendicular to the nasal septum. The slices should sufficiently cover the face from the glabella down to the body of the mandible. Slice and phase oversampling should be applied to avoid wrap-around artifacts.

TR 6.9 | TE 2.39 4.77 | FLIP 12 | NEX 2 | SLICE .7 MM | MATRIX 256X256 | FOV 170-180 | PHASE R>L | SLICES 200 | OVERSAMPLE 10% and100% |
T2 space stir 3D axial 1mm isotropic SFOV
Plan the axial slices on the sagittal plane and angle the planning block parallel to the hard palate. Check the planningg block in the other two planes. An appropriate angle must be provided in the coronal plane, perpendicular to the nasal septum. The slices should sufficiently cover the face from the glabella down to the body of the mandible. Slice and phase oversampling should be applied to avoid wrap-around artifacts.

Parameters
TR 2000-2600 | TE 200-250 | FLIP 35 | NEX 1.5 | SLICE 1 MM | MATRIX 256X256 | FOV 180-200 | PHASE R>L | GAP 10% | TI 130 |


