HASTE/Single-Shot FSE/Single-Shot TSE/FASE/EXPRESS
Half-Fourier-Acquired Single-shot Turbo Spin Echo (HASTE) is a turbo spin-echo technique used for the sequential acquisition of high-resolution T2-weighted images. HASTE employs a single-shot technique to acquire sufficient data for an entire image within a single TR. The HASTE imaging method utilizes a technique called half-Fourier in phase, where it collects only half of the lines in k-space and extrapolates the rest. A HASTE sequence can produce 2D slices in less than a second.
HASTE MRI Physics
HASTE is a variation of the turbo spin-echo (TSE) or fast spin-echo (FSE) sequence. Instead of acquiring multiple echoes after a single excitation as in TSE, HASTE acquires a single echo for each excitation. To accelerate image acquisition, HASTE employs a half-Fourier technique. In this approach, only slightly over half the k-space data (k-space represents spatial-frequency data from which MR images are reconstructed) is physically acquired, exploiting the inherent symmetry of k-space to reconstruct the full image. As the central k-space data predominantly determines image contrast, acquiring this information rapidly helps in reducing motion-induced artifacts.
HASTE MRI image appearance
HASTE MRI, produces images where fluid-filled spaces within the body prominently stand out. One can easily identify HASTE images by spotting these bright fluid regions. This includes the cerebrospinal fluid seen in the brain’s ventricles and the spinal canal, free fluid in the abdomen, the gall bladder and common bile duct’s liquid content, synovial fluid within joints, and the urinary tract and bladder’s fluid. Moreover, edema or any pathological fluid accumulations will also appear distinctly bright.
In distinguishing HASTE from TrueFISP sequences, a significant pointer is the appearance of blood vessels. While they emerge dark in HASTE images, they are bright in TrueFISP. However, it’s crucial to note that TrueFISP sequences are more susceptible to artifacts, specifically susceptibility and chemical shift artifacts.
Tissues and their Haste appearance
Brain:
- CSF: Bright.
- Fat: Bright.
- White Matter: Intermediate to dark.
- Gray Matter: Intermediate to dark.
- Bone (skull): Dark.
- Bone Marrow: Intermediate to bright.
- Blood Vessels: Mostly Dark.
- Pituitary Gland: Intermediate to dark.
- Choroid Plexus: Intermediate to dark.
- Cerebellum: Intermediate to dark.
- Brain Stem: Intermediate to dark.
- Sinuses: Dark (air-filled).
- Thalamus, Putamen, Hippocampus, Caudate Nucleus: Intermediate to dark.
- Corpus Callosum: Intermediate to dark.
- Pineal Gland: Intermediate to dark.
Spine:
- Spinal Cord: Intermediate to dark.
- CSF: Bright.
- Bone: Dark.
- Bone Marrow: Intermediate to bright.
- Intervertebral Disc: Intermediate
- Ligaments: Intermediate to Dark.
- Nerve Roots: Intermediate.
Abdomen and Pelvis:
- Liver: Intermediate.
- Gallbladder and Common Bile Duct: Bright.
- Spleen: Intermediate.
- Kidney: Intermediate.
- Ureters: Intermediate.
- Pancreas: Intermediate to dark.
- Urinary Bladder: Bright.
- Prostate: Intermediate.
- Uterus: Intermediate to bright.
Musculoskeletal:
- Muscle: Intermediate to dark.
- Bone: Dark (low signal).
- Bone Marrow: Intermediate to bright.
- Blood Vessels: Mostly Dark.
- Fat: bright.
- Ligaments: Intermediate to dark.
- Nerve Roots: Intermediate.
- Cartilage: Intermediate to dark.
- Synovial Fluid: Bright.
- Tendons: Intermediate to dark.
Use
- Very useful for MRCP imaging
- Very useful for urography imaging
- Very useful for sialography imaging
- Very useful for MRCP imaging
- Very useful for abdominal imaging
- Very useful for small bowel and MR colonoscopy imaging
- Very useful for chest imaging
- Useful for brain imaging (to acquire fast scans in uncooperative patients)
- Useful for liver imaging
HASTE fat saturated axial sequence used in MRCP imaging

HASTE coronal sequence used in enterography imaging

HASTE fat saturated coronal sequence used in urography imaging
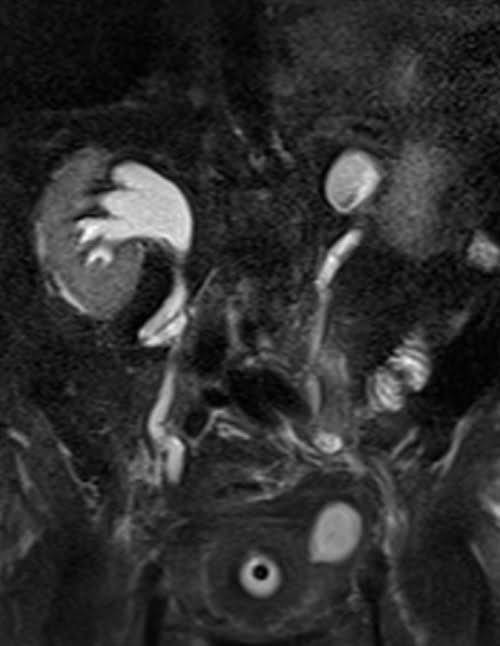
HASTE fat saturated coronal 60 mm sequence used in MRCP imaging

HASTE coronal 30 mm sequence used in sialography imaging imaging

HASTE coronal 60 mm sequence used in urography imaging

HASTE axial 5 mm sequence used in uncooperative patients brain imaging



