ZOOMit DWI: Physics and Applications
ZOOMit DWI (Diffusion Weighted Imaging) is an advanced MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) technique designed to provide high-resolution, diffusion-weighted images of specific regions of interest. Unlike traditional DWI, which captures larger anatomical areas and can suffer from susceptibility artifacts, ZOOMit DWI narrows the field of view (FOV) to target and magnify particular regions, ensuring clearer images with enhanced detail and reduced artifacts.
Physics of ZOOMit DWI
The fundamental principle behind any DWI technique, including ZOOMit, is the diffusion or the random motion of water molecules in tissues. This motion can be influenced by the microstructure of the tissue, and when probed with magnetic gradients, can result in signal changes that provide insight into this microstructure.
ZOOMit employs a technique called “2D spatially selective RF (radiofrequency) excitation.” In standard MRI, the entire slice is excited uniformly. However, with 2D spatially selective RF excitation, only a specific region within the slice is excited. This leads to several advantages:
Reduced Field of View (FOV): By focusing only on a specific region, the field of view is reduced, which allows for higher resolution imaging of the targeted area.
Reduced Susceptibility Artifacts: With a smaller FOV, susceptibility-induced artifacts (often seen near air-tissue interfaces) are minimized, leading to clearer images.
Shorter Echo Train Length: A reduced FOV means fewer k-space lines, leading to shorter echo train lengths and further reduction in susceptibility artifacts.
ZOOMit DWI Applications
- Neuroimaging: ZOOMit DWI can be used to focus on smaller regions within the brain, providing detailed images of areas like the hippocampus, brainstem, or specific lesions. This is particularly beneficial in conditions like temporal lobe epilepsy, where the focus lies in a small region.
- Spinal Imaging: The spinal cord, given its slender structure, can benefit greatly from ZOOMit imaging, providing clear delineations of cord lesions or tumors.
- Musculoskeletal Imaging: For detailed examination of small joints, ligament injuries, or small bone lesions, ZOOMit can provide the required high-resolution images.
- Breast Imaging: When a suspicious lesion is identified in standard imaging, ZOOMit DWI can offer a high-resolution view of the lesion, aiding in characterization and biopsy planning.
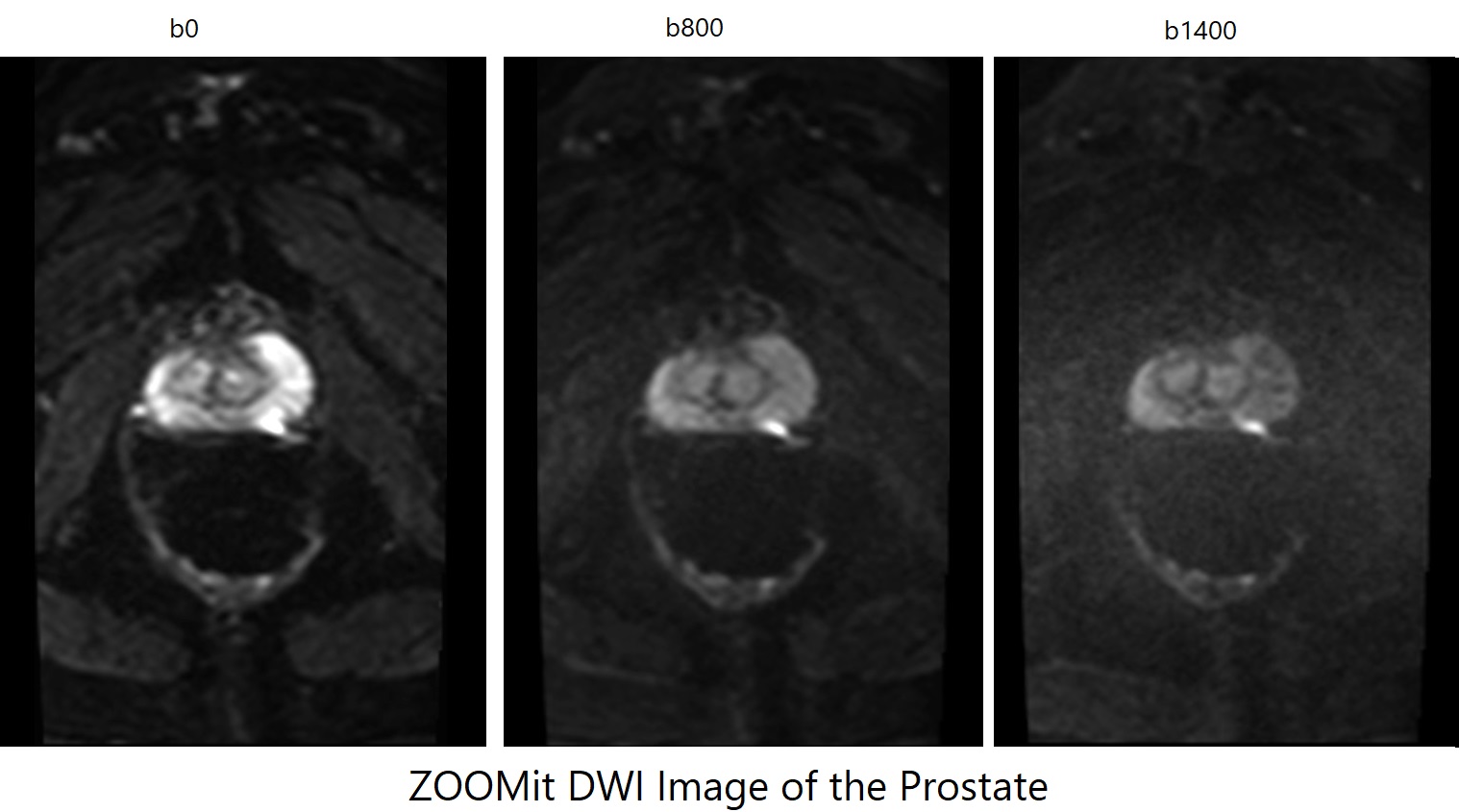
- Prostate Imaging: Detailed imaging of the prostate, especially in the presence of small lesions, can be achieved using ZOOMit DWI, leading to early and accurate diagnoses.
- Pelvic Imaging: For conditions like endometriosis or small pelvic tumors, ZOOMit offers a focused view, providing clinicians with detailed information.
ZOOMit DWI Axial b0 Image of Neck

ZOOMit DWI Axial b800 Image of Neck

ZOOMit DWI Axial ADC Image of Neck

ZOOMit DWI Axial b0 Image of Prostate

ZOOMit DWI Axial b800 Image of Prostate

ZOOMit DWI Axial b1400 Image of Prostate
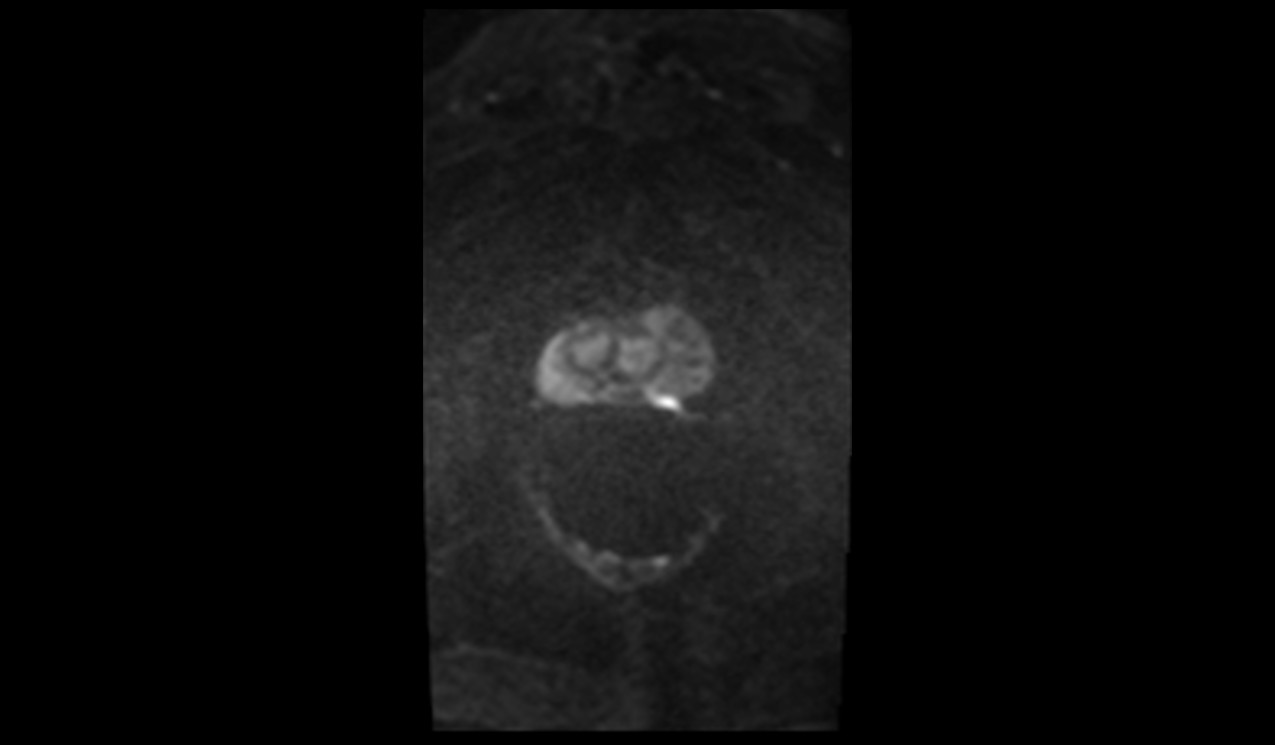
ZOOMit DWI Axial ADC Image of Prostate

References
- Yıldırım, İ. O., Sağlık, S., & Çelik, H. (2017). Conventional and ZOOMit DWI for Evaluation of Testis in Patients With Ipsilateral Varicocele. American Journal of Roentgenology, 208(5).
- Tang, S., Fu, C., Chen, H., Xiao, E., Long, Y., & Bian, D. (2023). Comparison of ZOOMit-DWI Sequence and Conventional DWI Sequence in Endometrial Cancer. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban, 48(1), 76-83. doi:10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2023.220018.
- Zhou, Q.-Q., Zhang, W., Yu, Y.-S., Li, H.-Y., Wei, L., Li, X.-S., He, Z.-Z., & Zhang, H. (2022). Comparative Study between ZOOMit and Conventional Intravoxel Incoherent Motion MRI for Assessing Parotid Gland Abnormalities in Patients with Early- or Mid-Stage Sjögren’s Syndrome. Korean Journal of Radiology, 23(4), 455–465.
