MRA Brain : Protocol and Planning
Introduction
MRA stands for magnetic resonance angiography. MRA of the brain is used to assess abnormalities in the arterial blood supply system of the brain. The most frequently employed method for assessing the brain’s arterial blood supply system is the three-dimensional (3D) time-of-flight (TOF) MRA. This technique offers advantages such as improved signal-to-noise ratio and shorter imaging times. One of the notable benefits of MRA brain is its simplicity, as it can be easily performed without the need for contrast administration.
Time-of-flight (TOF) MRA
Time-of-flight (TOF) MRI is a technique used in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to acquire high-resolution images of blood vessels. It takes advantage of the differences in arrival times of the MRI signal from different locations within the body. By applying selective radiofrequency pulses and gradients, the signal from stationary tissue is suppressed while the signal from flowing blood is preserved. This leads to high contrast between blood vessels and surrounding tissue. TOF MRI provides information about blood flow and is commonly used in the evaluation of vascular structures, such as detecting aneurysms, stenoses, and arteriovenous malformations. It allows for non-invasive assessment of blood vessels and can visualize them with high spatial resolution.
Indications for MRA brain
- Aneurysm, Stroke, Vasospasm, Vasculitis
- Internal Carotid Artery Occlusion and Stenosis
- Cerebral Artery Occlusion and Stenosis
- Basilar Artery Occlusion and Stenosis
- Arteriovenous malformation (AVM)
- Atherosclerotic Disease
Contraindications MRA Brain
- Any electrically, magnetically or mechanically activated implant (e.g. cardiac pacemaker, insulin pump biostimulator, neurostimulator, cochlear implant, and hearing aids)
- Intracranial aneurysm clips (unless made of titanium)
- Pregnancy (risk vs benefit ratio to be assessed)
- Ferromagnetic surgical clips or staples
- Metallic foreign body in the eye
- Metal shrapnel or bullet
Patient preparation for MRA brain
- A satisfactory written consent form must be taken from the patient before entering the scanner room
- Ask the patient to remove all metal objects including keys, coins, wallet, cards with magnetic strips, jewellery, hearing aid and hairpins
- If possible provide a chaperone for claustrophobic patients (e.g. relative or staff )
- Offer earplugs or headphones, possibly with music for extra comfort
- Explain the procedure to the patient
- Instruct the patient to keep still
- Note the hight and weight of the patient
Positioning for MRA brain
- Head first supine
- Position the head in the head coil and immobilise with cushions
- Give cushions under the legs for extra comfort
- Centre the laser beam localiser over the glabella

Recommended MRA Brain Protocols, Parameters, and Planning
localiser
A three-plane localizer must be taken at the beginning to localize and plan the sequences. Localizers are usually less than 25 seconds and are T1-weighted low-resolution scans.
T2 tse axial
Plan the axial slices on the sagittal plane and angle the planning block parallel to the genu and splenium of the corpus callosum. Check the planning block in the other two planes and ensure an appropriate angle is provided in the coronal plane for a tilted head (perpendicular to the line of the 3rd ventricle and brainstem). The slices should be sufficient to cover the entire brain from the vertex to the line of the foramen magnum.
Parameters

TR 3000-4000 | TE 100-120 | SLICE 5MM | FLIP 130-150 | PHASE R>L | MATRIX 320X320 | FOV 210-230 | GAP 10% | NEX(AVRAGE) 2 |
3D time-of-flight (TOF)
Plan the axial 3D block on the sagittal plane, angling the planning block parallel to the genu and splenium of the corpus callosum. Ensure that the slices are sufficient to cover the entire Circle of Willis, extending from 1 cm above the corpus callosum up to the line of the foramen magnum. Verify the planning block in the other two planes and ensure an appropriate angle is maintained in the coronal plane, perpendicular to the line of the 3rd ventricle and brainstem. To reduce venous contamination in the resulting image, TOF sequences use saturation bands on top of the axial block.
Parameters
TR 30-40 | TE 5-9 | FLIP 25 | NEX 1 | SLICE .7MM | MATRIX 256×256 | FOV 250 | PHASE R>L | GAP 33% | MTC ON |

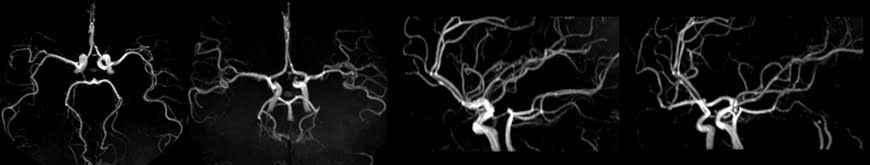
Maximum intensity projection (MIP)
MIP (Maximum Intensity Projection) is a widely used post-processing technique in MRI vascular studies. It involves the reconstruction of a 2D projection image from 3D volumetric data using a ray-tracing algorithm. This algorithm selects the highest intensity signal within the examined volume at each location and assigns it to a white pixel in the resulting image. By utilizing the maximum intensity values, MIP provides a visual representation that emphasizes the blood vessels’ highest signal intensity, enhancing their visibility and aiding in the evaluation of vascular structures. MIP images are particularly valuable in identifying vascular abnormalities, such as stenoses, aneurysms, and vascular malformations, as they highlight the regions with the strongest contrast enhancement.