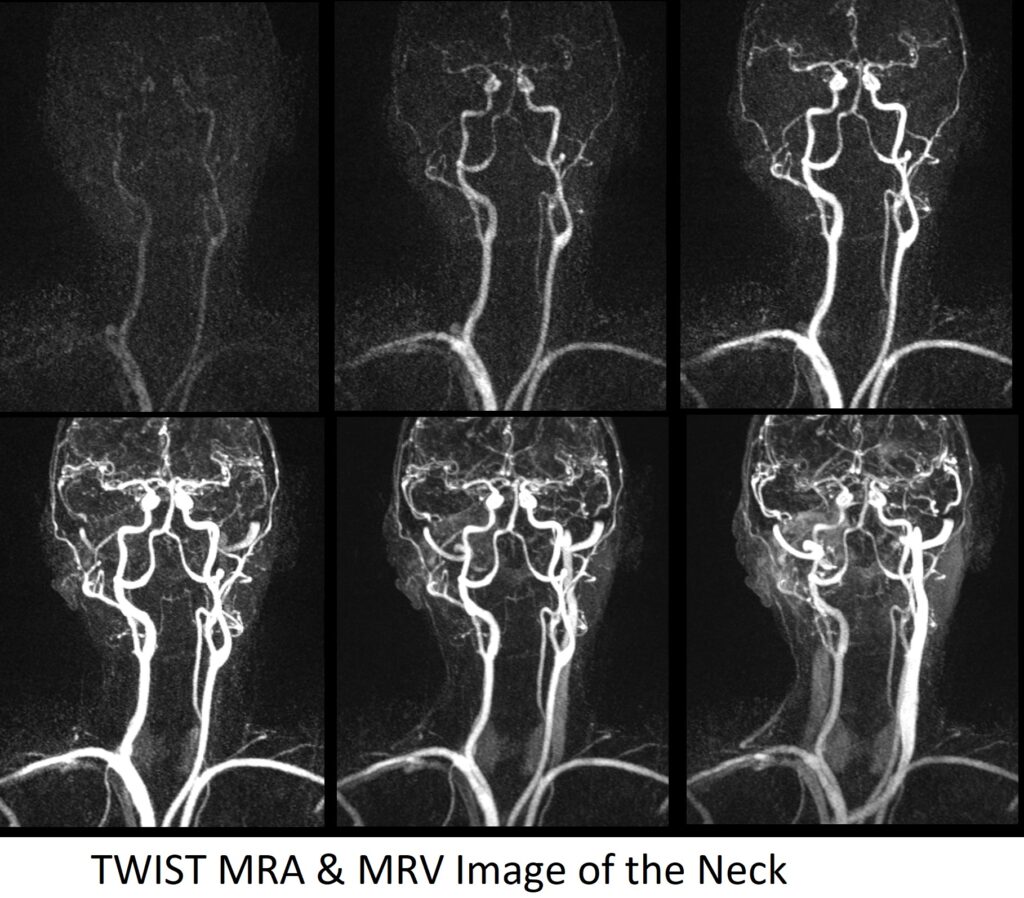
TWIST\TRICKS MRA Carotid and Subclavian Arteries
TWIST (Time-resolved Angiography With Interleaved Stochastic Trajectories) MRA
TWIST (Time-resolved Angiography With Interleaved Stochastic Trajectories) is an advanced and innovative 3D Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) technique that offers exceptionally high temporal (sub-second) and spatial resolution (sub-millimeter). This unique capability allows for the acquisition of multiple arterial, mixed, and venous phase images, capturing the passage of a contrast agent through the vascular anatomy in real-time.
TWIST MRA is based on a special k-space sampling technique. The k-space, a mathematical representation of image data, is divided into two regions. The central region of k-space provides information related to image contrast, while the peripheral region primarily contributes to achieving high spatial resolution.
The acceleration of the sequence acquisition is achieved by more frequently sampling k-space lines in the center during the passage of the contrast medium bolus through the covered 3D volume. This random and interleaved sampling technique optimizes both temporal and spatial resolution, enabling the real-time visualization of blood flow dynamics and vascular structures.
TWIST MRA is particularly beneficial in pediatric populations with soft-tissue vascular anomalies in the head and neck region. Compared to conventional contrast-enhanced MRI (CE-MRI), TWIST MRA with gadofosveset trisodium, a blood-pool contrast agent, offers detailed temporal information of VA hemodynamics and flow characteristics without the need for invasive procedures.
Indications for TWIST MRA carotid and subclavian arteries
- Thoracic outlet syndrome
- Subclavian vein thrombosis
- Subclavian steal syndrome
- Pre-pacemaker placement
- Pre-op for dialysis fistula
- Subclavian artery dissection
- Subclavian stenosis
- Arm swelling
Contraindications
- Any electrically, magnetically or mechanically activated implant (e.g. cardiac pacemaker, insulin pump biostimulator, neurostimulator, cochlear implant, and hearing aids)
- Intracranial aneurysm clips (unless made of titanium)
- Pregnancy (risk vs benefit ratio to be assessed)
- Ferromagnetic surgical clips or staples
- Metallic foreign body in the eye
- Metal shrapnel or bullet
Patient preparation for TWIST MRA carotid and subclavian arteries
- A satisfactory written consent form must be taken from the patient before entering the scanner room
- Ask the patient to remove all metal objects including keys, coins, wallet, cards with magnetic strips, jewellery, hearing aid and hairpins
- Ask the patient to undress and change into a hospital gown
- Instruct the patient to hold their breath for the breath hold scans (its better to coach the patient two to three times before starting the scan)
- An intravenous line must be placed with extension tubing extending out of the magnetic bore intravenous line must be placed in the unaffected side e.g if the problem exists in RT subclavian the canula should be in LT side
- Contrast injection risk and benefits must be explained to the patient before the scan
- Gadolinium should only be given to the patient if GFR is > 30
- Claustrophobic patients may be accompanied into the scanner room e.g. by staff member or relative with proper safety screening
- Offer headphones for communicating with the patient and ear protection
- Explain the procedure to the patient and answer questions
- Note down the weight of the patient
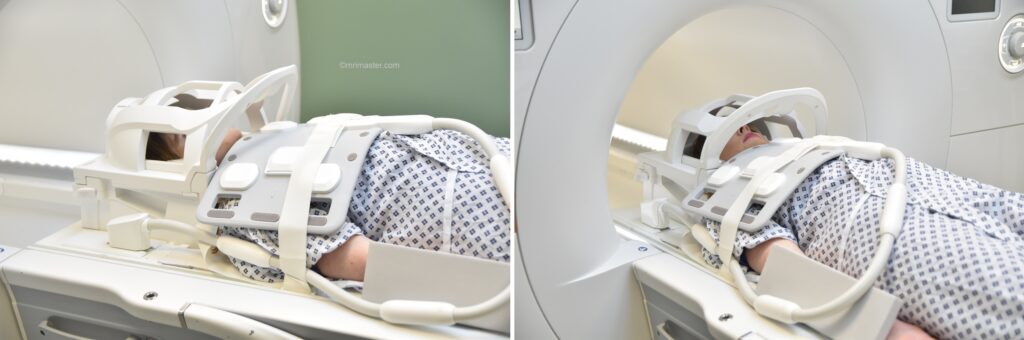
Positioning for MRA of carotid and subclavian arteries
- Position the patient in supine position with head pointing towards the magnet (head first supine)
- Position the patient over the spine, head, and neck coil, and place the head and neck, along with the body coil or large flex coil, over the neck and upper chest.
- Give cushions under the legs for extra comfort
- Centre the laser beam localiser over sternoclavicular joint
Recommended TWIST MRA Carotid and subclavian Protocols, Parameters, and Planning
localiser arm down MRA and MRV of subclavians
A three-plane TrueFISP localizer must be taken initially to localize and plan the sequences. These are fast single-shot localizers with under 25s acquisition time, which are excellent for localizing vascular structures. Take at least 5-8 slices in all planes to get the best results.

TWIST coronal 1mm 3pre and 25 post
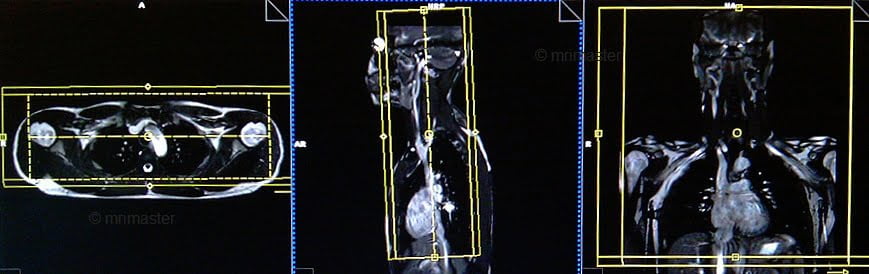
Plan the coronal 3D block on the sagittal plane, angling the positioning block parallel to the carotid arteries and veins (alternatively, parallel to the cervical spine). Check the positioning block in the other two planes. Provide an appropriate angle in the axial plane (parallel to the right and left shoulder joint). The slices must be sufficient to cover the carotids and subclavians from the anterior chest wall to the spinous process of the vertebrae. The Field of View (FOV) must be large enough to cover both shoulder joints. To prevent wrap-around artifacts, utilize phase oversampling and slice oversample. During the image acquisition, instruct the patient to breathe shallowly.
Parameters
TR 4-5 | TE 1.25 | FLIP 14 | NEX 1 | SLICE 1MM | MATRIX 320X320 | FOV 320-400 | PHASE R>L | DYNAMIC 28 SCAN | IPAT ON |
A dynamic TWIST sequence consists of 26 1mm 3D scans, with each acquisition taking around 3-4 seconds. The contrast injection must be administered after the third dynamic sequence.
T1 VIBE DIXON AXIAL 2MM
Plan the coronal slices on the sagittal plane and angle the positioning block horizontally across the chest. Check the positioning block in the other two planes and provide an appropriate angle in the axial plane (horizontally across the chest). The slices must be sufficient to cover the neck and upper chest from the galbella to the mid-heart level. The Field of View (FOV) must be large enough to cover both shoulder joints. Phase oversampling and slice oversample must be used to avoid wrap-around artifacts. Instruct the patient to hold their breath during image acquisition.
Parameters
TR 6-7 | TE 2.39 4.77 | FLIP 10 | NXA 1 | SLICE 3 MM | MATRIX 320×320 | FOV 320-400 | PHASE A>P | OVERSAMPLE 20% | BH NO |