MRI Sternum
Indications for sternal mri
- Degenerative and inflammatory conditions(eg.osteoarthritis, osteomyelitis, septic arthritis)
- Traumatic and iatrogenic conditions (eg. sternal fractures sternoclavicular dislocation)
- Congenital anomalies (eg. pectus carinatum, tilted sternum, sternal sclerotic band and cleft,sternal foramen)
- Postsurgical complications
- Benign lesions
- Neoplasms
- Metastases
Contraindications
- Any electrically, magnetically or mechanically activated implant (e.g. cardiac pacemaker, insulin pump biostimulator, neurostimulator, cochlear implant, and hearing aids)
- Intracranial aneurysm clips (unless made of titanium)
- Pregnancy (risk vs benefit ratio to be assessed)
- Ferromagnetic surgical clips or staples
- Metallic foreign body in the eye
- Metal shrapnel or bullet
Patient preparation for MRI Sternum
- A satisfactory written consent form must be taken from the patient before entering the scanner room
- Ask the patient to remove all metal object including keys, coins, wallet, any cards with magnetic strips, jewellery, hearing aid and hairpins
- Ask the patient to undress and change into a hospital gown
- Contrast injection risk and benefits must be explained to the patient before the scan
- Gadolinium should only be given to the patient if GFR is > 30
- If possible provide a chaperone for claustrophobic patients (e.g. relative or staff )
- Offer earplugs or headphones, possibly with music for extra comfort
- Explain the procedure to the patient
- Instruct the patient to keep still
- Note down the weight of the patient
Positioning for MRI Sternum
- Position the patient in prone position with head pointing towards the magnet (head first prone)
- Position the patient’s chest over the spine coil
- Now, place the large flex coil over the chest as shown in the picture.
- Give cushions under the forehead and legs for extra comfort
- Centre the laser beam localiser over T5 vertebra

Recommended MRI Sternum Protocols, Parameters, and Planning
MRI Sternum localiser 1
To localize and plan the sequences, it is essential to acquire a three-plane T2 HASTE localizer initially. These fast single-shot localizers have an acquisition time of under 25 seconds and are highly effective in accurately localizing chest and abdominal structures.
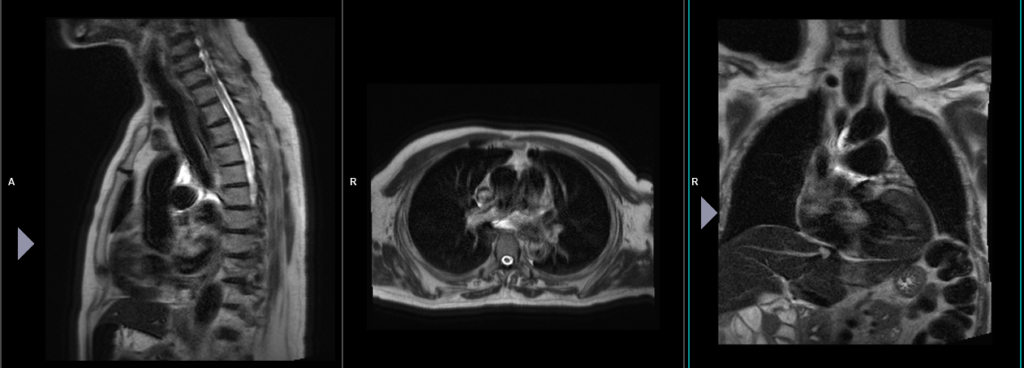
MRI Sternum localiser 2
For the proper planning of sternum scans, it is necessary to include a second two-plane localizer. The two-plane localizer should be planned on the sagittal plane. Align the planning block parallel to the sternum for a true coronal localizer and perpendicular to the sternum for the axial localizer.
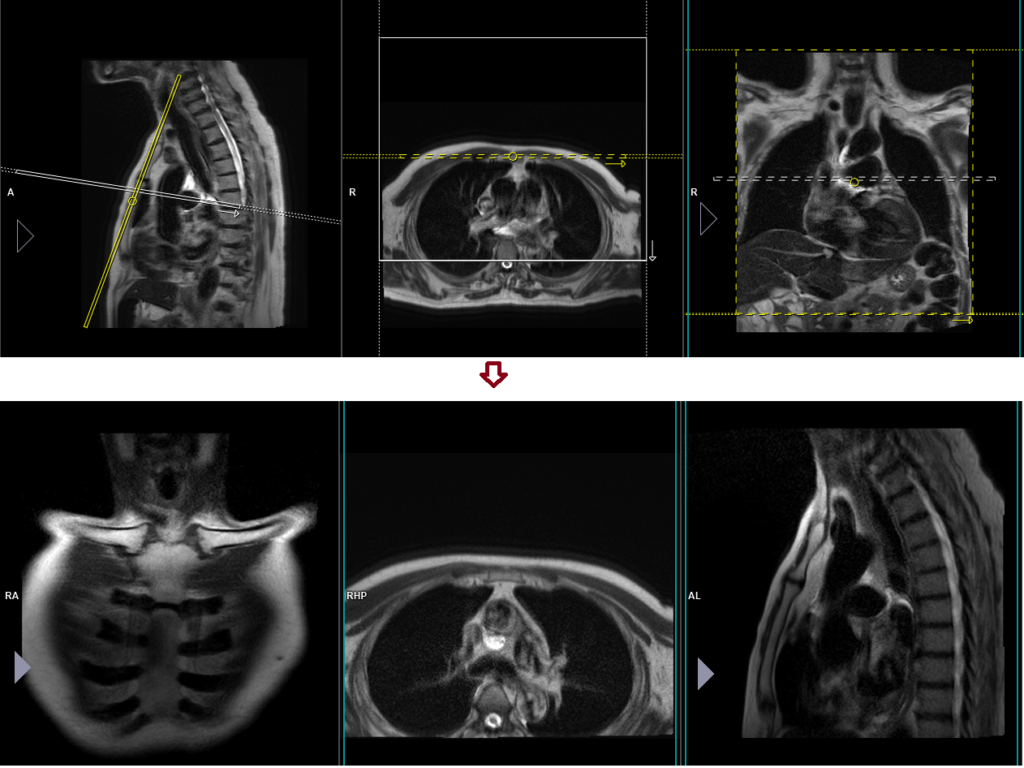
T2 tse sagittal 3mm SFOV
Plan the sagittal slices on the coronal plane; angle the planning block parallel to the body of the sternum. Verify the positioning block in the other two planes. Ensure an appropriate angle is set in the axial plane, perpendicular to the sternum’s body. The slices should adequately cover the sternum from one sternoclavicular joint to the other. To minimize ghosting artifacts caused by heartbeats and breathing, consider utilizing a saturation band over the chest. If a radial k-space sequence (blade) is unavailable, opt for head-to-feet phase encoding. In our department, we prefer using blade scans for this purpose.
Parameters
TR 3000-4000 | TE 100-120 | SLICE 3 MM | FLIP 130-150 | PHASE H>F | MATRIX 256X256 | FOV 200-230 | GAP 10% | NEX(AVRAGE) 2 |
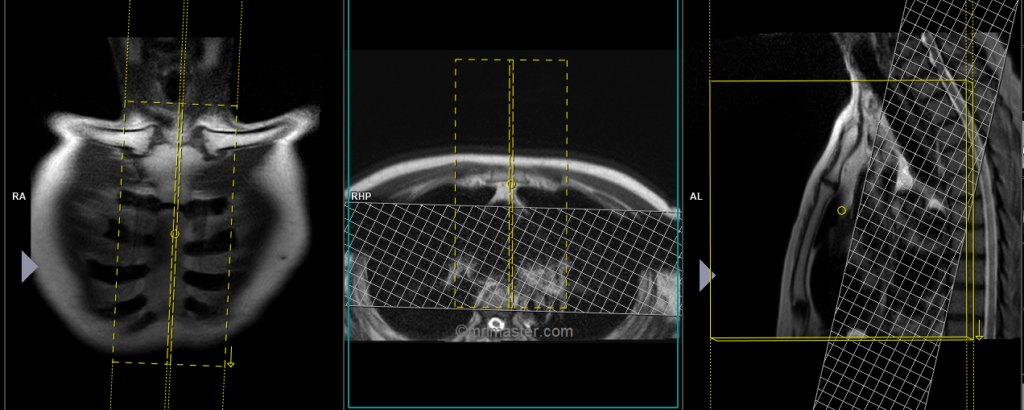
T1 tse coronal 3mm SFOV
Plan the coronal slices on the sagittal plane and angle the planning block parallel to the sternum. Verify the planning block in the other two planes. Maintain an appropriate angle in the axial plane, horizontally across the sternum. Ensure that the slices adequately cover the sternum from the front to the back. To minimize ghosting artifacts caused by breathing and heart motion, consider using a saturation band over the chest. Use right to left phase encoding to avoid artifacts from the chest.

Parameters
TR 400-600 | TE 15-25 | SLICE 3 MM | FLIP 90 | PHASE R>L | MATRIX 256X256 | FOV 200-2230 | GAP 10% | NEX(AVRAGE) 2 |
T2 stir coronal 3mm SFOV
Plan the coronal slices on the sagittal plane and angle the planning block parallel to the sternum. Verify the planning block in the other two planes. Maintain an appropriate angle in the axial plane, horizontally across the sternum. Make sure the slices adequately cover the sternum from the front to the back. To minimize ghosting artifacts caused by breathing and heart motion, consider using a saturation band over the chest. If a blade sequence is not employed, apply right to left phase encoding.

Parameters
TR 4000-5000 | TE 110 | FLIP 130 | NEX 2 | SLICE 3 MM | MATRIX 256X256 | FOV 200-220 | PHASE R>L | GAP 10% | TI 150 |
T1 tse axial 3mm SFOV
Plan the axial slices on the sagittal plane and angle the planning block perpendicular to the sternum. Verify the planning block in the other two planes. Ensure an appropriate angle is given in the coronal plane, perpendicular to the body of the sternum. The slices should sufficiently cover the sternum, ranging from two slices above the suprasternal notch down to the lower border of the xiphoid process. To minimize ghosting artifacts resulting from breathing and heart motion, apply a saturation band over the chest. Please use a right-to-left phase encoding direction to avoid artifacts originating from the chest.

Parameters
TR 400-600 | TE 15-25 | SLICE 3 MM | FLIP 90 | PHASE R>L | MATRIX 256X256 | FOV 200-230 | GAP 10% | NEX(AVRAGE) 2 |
T2 stir axial 3mm SFOV
Plan the axial slices on the sagittal plane and angle the planning block perpendicular to the sternum. Verify the planning block in the other two planes. Ensure an appropriate angle is given in the coronal plane, perpendicular to the body of the sternum. The slices should sufficiently cover the sternum, ranging from two slices above the suprasternal notch down to the lower border of the xiphoid process. To minimize ghosting artifacts resulting from breathing and heart motion, apply a saturation band over the chest. Please use a right-to-left phase encoding direction to avoid artifacts originating from the chest.

Parameters
TR 4000-5000 | TE 110 | FLIP 130 | NEX 2 | SLICE 3 MM | MATRIX 256X256 | FOV 200-220 | PHASE R>L | GAP 10% | TI 150 |
