Ankle MRI : Protocol and Planning
Indications for ankle MRI scan
- Marrow abnormalities (eg. bone contusions, osteonecrosis, marrow edema syndromes, and stress fractures)
- Synovial-based disorders ( e.g. synovitis, tenosynovitis, bursitis, and ganglion cysts)
- Congenital and developmental conditions( eg.dysplasia, tarsal coalition)
- Achilles tendon disorders (e.g.tears, tendonitis, tendinopathy)
- Infections of bone, joint or soft tissue (e.g. osteomyelitis)
- Osteochondral and articular cartilage abnormalities
- Abnormalities of other hindfoot tendons
- Plantar fasciitis and fascial rupture
- Neoplasms of bone, joint or soft tissue
- Posterior tibial tendon disorders
- Peroneal tendon disorders
- Intra-articular loose body
- Sinus tarsi syndrome
- Avascular necrosis
- Fibromatosis
Contraindications
- Any electrically, magnetically or mechanically activated implant (e.g. cardiac pacemaker, insulin pump biostimulator, neurostimulator, cochlear implant, and hearing aids)
- Intracranial aneurysm clips (unless made of titanium)
- Pregnancy (risk vs benefit ratio to be assessed)
- Ferromagnetic surgical clips or staples
- Metallic foreign body in the eye
- Metal shrapnel or bullet
Patient preparation ankle MRI scan
- A satisfactory written consent form must be taken from the patient before entering the scanner room
- Ask the patient to remove all metal object including keys, coins, wallet, any cards with magnetic strips, jewellery, hearing aid and hairpins
- If possible provide a chaperone for claustrophobic patients (e.g. relative or staff )
- Offer earplugs or headphones, possibly with music for extra comfort
- Explain the procedure to the patient
- Instruct the patient to keep still
- Note the weight of the patient
Positioning for ankle MRI scan
- Position the patient in supine position with feet pointing towards the magnet (feet first supine)
- Position the ankle in the foot and ankle coil (use knee coil if ankle coil is not available) and lock it properly (Ankle should be at 90° position)
- Securely tighten the foot using cushions to prevent movement
- Give a pillow under the head for extra comfort
- Centre the laser beam localiser over ankle joint

Recommended Ankle MRI Protocols and Planning
Ankle MRI localiser
A three-plane localizer must be taken at the beginning to localize and plan the sequences. Localizers are usually less than 25 seconds and consist of T1-weighted, low-resolution scans.

PD tse axial 3 mm
Plan the axial slices on the coronal plane and angle the positioning block parallel to the tibio-talar joint. Check the positioning block in the other two planes. An appropriate angle must be given in the sagittal plane, parallel to the tibio-talar joint. The slices should be sufficient to cover the ankle joint from 2 inches above the tibio-talar joint down to the plantar aspect of the foot. Using saturation bands above the axial block can reduce arterial pulsation artefacts.

Parameters
TR 3000-4000 | TE 15-20 | SLICE 3 MM | FATSAT OFF | PHASE A>P | MATRIX 320X320 | FOV 130-150 | GAP 10% | NEX(AVRAGE) 2 |
T2 stir axial 3mm
Plan the axial slices on the coronal plane and angle the positioning block parallel to the tibio-talar joint. Check the positioning block in the other two planes. An appropriate angle must be given in the sagittal plane, parallel to the tibio-talar joint. The slices should be sufficient to cover the ankle joint from 2 inches above the tibio-talar joint down to the plantar aspect of the foot. Using saturation bands above the axial block can reduce arterial pulsation artefacts.

Parameters
TR 4000-6000 | TE 110 | FLIP 150 | NEX 2 | SLICE 3 MM | MATRIX 256X256 | FOV 130-150 | PHASE A>P | GAP 10% | TI 130 |
T1 tse sagittal 3mm
Plan the sagittal slices on the axial plane and angle the positioning block perpendicular to the line between the medial and lateral malleoli. Check the positioning block in the other two planes. An appropriate angle must be given in the coronal plane, parallel to the tibia. The slices must be sufficient to cover the ankle joint from the outer border of the medial malleolus to the outer border of the lateral malleolus. Using saturation bands above the axial block can reduce arterial pulsation artefacts.

Parameters
TR 400-600 | TE 15-25 | SLICE 3 MM | FLIP 150 | PHASE A>P | MATRIX 320X320 | FOV 150-170 | GAP 10% | NEX(AVRAGE) 2 |
T2 stir sagittal 3mm
Plan the sagittal slices on the axial plane and angle the positioning block perpendicular to the line between the medial and lateral malleoli. Check the positioning block in the other two planes. An appropriate angle must be given in the coronal plane, parallel to the tibia. The slices must be sufficient to cover the ankle joint from the outer border of the medial malleolus to the outer border of the lateral malleolus. Using saturation bands above the axial block can reduce arterial pulsation artefacts.

Parameters
TR 4000-6000 | TE 110 | FLIP 150 | NEX 2 | SLICE 3 MM | MATRIX 256X256 | FOV 150-170 | PHASE A>P | GAP 10% | TI 150 |
PD fat saturated coronal 3mm
Plan the coronal slices on the axial plane; angle the positioning block parallel to the line along the medial and lateral malleoli. Check the positioning block in the other two planes. An appropriate angle must be given in the sagittal plane (parallel to the tibia). Slices must be sufficient to cover the ankle joint from the Achilles tendon to the midfoot. Using saturation bands above the axial block can reduce arterial pulsation artefacts.
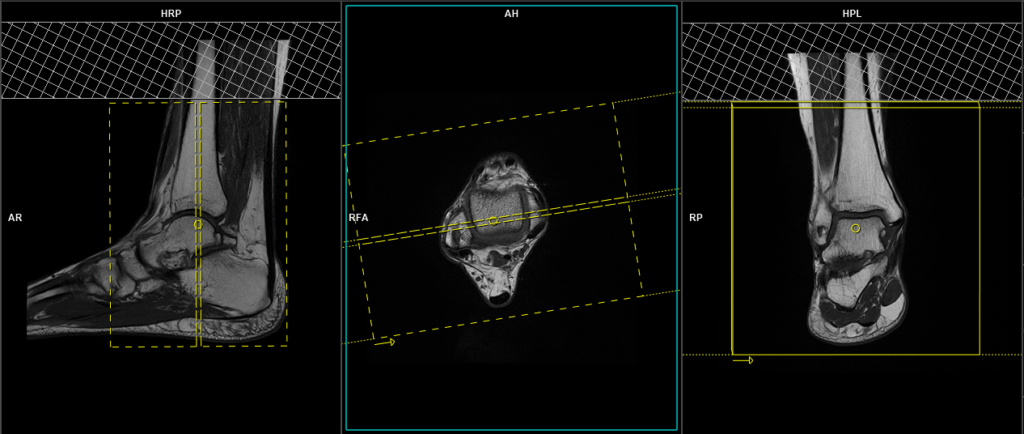
Parameters
TR 3000-5000 | TE 15-20 | SLICE 3 MM | FATSAT ON | PHASE R>L H>F | MATRIX 320X320 | FOV 150-170 | GAP 10% | NEX(AVRAGE) 2 |
