Paranasal Sinuses MRI
Indications for paranasal sinuses (PNS) MRI scan
- For the evaluation of intracranial extension of sinonasal disease.
- For the evaluation of malignant tumors of the sinonasal tract
- For the evaluation of sinus extension of orbital cellulitis and abscess
- For the evaluation of brain abscess due to sinusitis
- Fibro-osseous lesions of sinuses
- Inverted papilloma
- Sinus infections
- Encephalocele
- Meningioma
- ENT tumour
- Keratocyst
- Mucocele
Contraindications paranasal sinuses (PNS) MRI scan
- Any electrically, magnetically or mechanically activated implant (e.g. cardiac pacemaker, insulin pump biostimulator, neurostimulator, cochlear implant, and hearing aids)
- Intracranial aneurysm clips (unless made of titanium)
- Pregnancy (risk vs benefit ratio to be assessed)
- Ferromagnetic surgical clips or staples
- Metallic foreign body in the eye
- Metal shrapnel or bullet
Patient preparation for paranasal sinuses MRI scan
- A satisfactory written consent form must be taken from the patient before entering the scanner room
- Ask the patient to remove all metal objects including keys, coins, wallet, cards with magnetic strips, jewellery, hearing aid and hairpins
- If possible provide a chaperone for claustrophobic patients (e.g. relative or staff )
- Contrast injection risk and benefits must be explained to the patient before the scan
- Gadolinium should only be given to the patient if GFR is > 30
- Offer earplugs or headphones, possibly with music for extra comfort
- Explain the procedure to the patient
- Instruct the patient to keep still
- Note the weight of the patient
Positioning for paranasal sinuses MRI scan
- Head first supine
- Position the head in the head coil and immobilise with cushions
- Give cushions under the legs for extra comfort
- Centre the laser beam localizer over the glabella

Recommended PNS Protocols, Parameters, and Planning
localiser
A three-plane localizer must be taken at the beginning to localize and plan the sequences. Localizers are usually less than 25 seconds and are T1-weighted low-resolution scans.

T2 tse axial 4mm
Plan the axial slices on the sagittal plane and position the block parallel to the genu and splenium of the corpus callosum. Verify the planning block in the other two planes and ensure that an appropriate angle is maintained in the coronal plane, making it perpendicular to the line of the midline of the brain and the 4th ventricle. Ensure that the number of slices is sufficient to cover the entire brain from the vertex to the line of the foramen magnum.This brain axial is very useful for the evaluation of intracranial extension of sinonasal disease.

Parameters
TR 3000-4000 | TE 100-120 | SLICE 4MM | FLIP 130-150 | PHASE R>L | MATRIX 320X320 | FOV 210-230 | GAP 10% | NEX(AVRAGE) 2 |
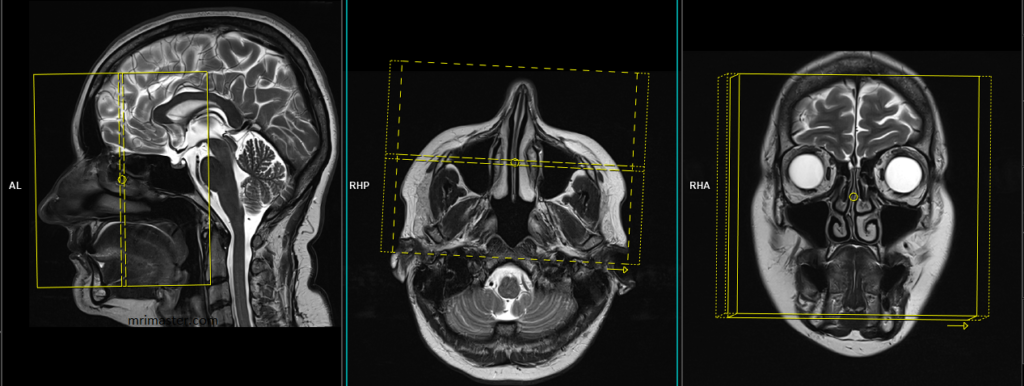
T2 STIR coronal 3mm small FOV
Plan the coronal slices on the sagittal plane; angle the planning block perpendicular to the hard palate. Check the positioning block in the other two planes. An appropriate angle must be given in the axial plane (perpendicular to the nasal septum). Slices must be sufficient to cover the entire sinuses from the tip of the nose to the brain stem.
Parameters
TR 4000-5000 | TE 110 | FLIP 150 | NEX 3 | SLICE 3 MM | MATRIX 256X256 | FOV 160-170 | PHASE R>L | GAP 10% | TI 150 |
T1 tse coronal 3mm small FOV
Plan the coronal slices on the sagittal plane; angle the planning block perpendicular to the hard palate. Check the planning block in the other two planes. An appropriate angle must be given in the axial plane (perpendicular to the nasal septum). Slices must be sufficient to cover the entire sinuses from the tip of the nose to the brain stem.

Parameters
TR 400-600 | TE 15-25 | SLICE 3 MM | FLIP 140 | PHASE R>L | MATRIX 256X256 | FOV 160-170 | GAP 10% | NEX(AVRAGE) 2 |
RESOLVE DWI coronal
Plan the coronal slices on the sagittal plane; angle the planning block perpendicular to the hard palate. Check the planning block in the other two planes. An appropriate angle must be given in the axial plane (perpendicular to the nasal septum). Slices must be sufficient to cover the entire sinuses from the tip of the nose to the brain stem.

RESOLVE DWI: RESOLVE is an advanced technique used to obtain high-quality and high-resolution DWI (diffusion-weighted imaging) images, particularly in body regions affected by susceptibility artifacts. It offers sharp imaging with minimal distortions and provides excellent spatial resolution. RESOLVE is especially valuable for evaluating smaller lesions in a wide range of DWI and DTI (diffusion tensor imaging) examinations. By combining RESOLVE with Simultaneous Multi-Slice (SMS) acceleration, acquisition time can be significantly reduced, improving both speed and imaging capabilities. RESOLVE finds application in various clinical fields, including neurology, oncology, and pediatric imaging. Its outstanding balance between imaging speed and quality makes it superior to other diffusion-weighted imaging sequences. Benefits of RESOLVE include high-quality DWI and DTI, reduced susceptibility and blurring artifacts, insensitivity to motion-induced phase errors, lower specific absorption rate (SAR) compared to TSE-based methods, and compatibility with iPAT for faster scans and further reduced distortions.
Parameters
TR 7000-9000 | TE 70 | FLIP 130 | NXA 1 2 | SLICE 3MM | MATRIX 192X192 | FOV 210-230 | PHASE R>L | GAP 10% | B VALUE 0 |
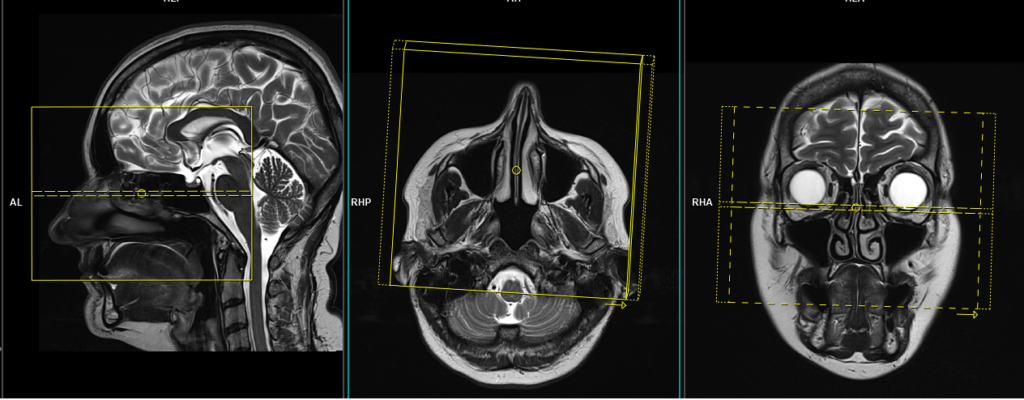
T2 STIR axial 3mm SFOV
Plan the axial slices on the sagittal plane and angle the planning block parallel to the hard palate. Check the planning block in the other two planes. An appropriate angle must be given in the coronal plane (perpendicular to the nasal septum). The slices must be sufficient to cover the entire sinuses, from the superior border of the frontal sinus down to the level of the lower lip.
Parameters
TR 4000-5000 | TE 110 | FLIP 150 | NEX 3 | SLICE 3 MM | MATRIX 256X256 | FOV 160-170 | PHASE R>L | GAP 10% | TI 150 |
T1 tse axial 3mm SFOV
Plan the axial slices on the sagittal plane and angle the planning block parallel to the hard palate. Check the planning block in the other two planes. An appropriate angle must be given in the coronal plane (perpendicular to the nasal septum). The slices must be sufficient to cover the entire sinuses, from the superior border of the frontal sinus down to the level of the lower lip.

Parameters
TR 400-600 | TE 15-25 | SLICE 3 MM | FLIP 140 | PHASE R>L | MATRIX 256X256 | FOV 160-170 | GAP 10% | NEX(AVRAGE) 3 |
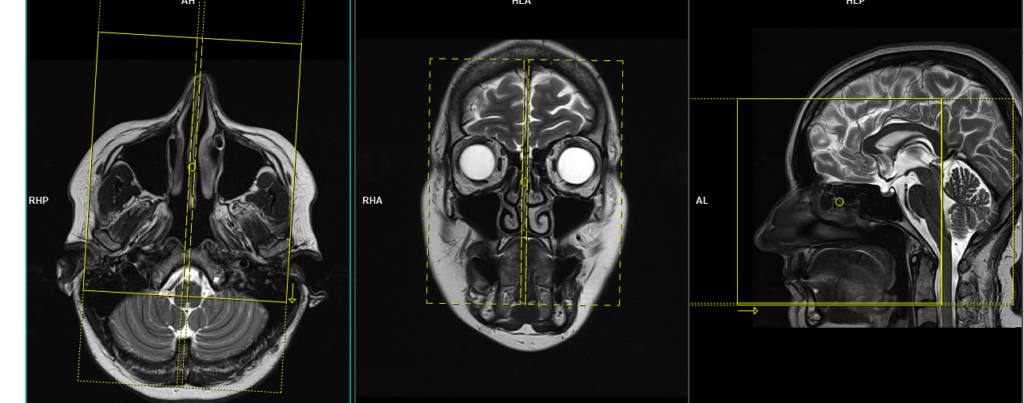
T2 tse sagittal 3mm SFOV
Plan the sagittal slices on the axial plane; angle the planning block parallel to the nasal septum. Check the planning block in the other two planes. An appropriate angle must be given in the coronal plane (parallel to the nasal septum). Slices must be sufficient to cover the entire sinuses from right to left.
Parameters
TR 4000-5000 | TE 100-120 | SLICE 3MM | FLIP 130-150 | PHASE A>P | MATRIX 288X256 | FOV 150-170 | GAP 10% | NEX(AVRAGE) 2 |
For contrast enhancement scans
Use T1-weighted sequences (T1 tse DIXON) in both axial and coronal planes after the administration of IV gadolinium DTPA injection (copy the planning outlined above). The document below provides access to the recommended dosage of gadolinium DTPA injection as advised by the manufacturer.
