Facial Nerve (3D Protocol) MRI
Indications for Facial nerve MRI scan
- Assessment of inflammatory disorders affecting the facial nerve.
- Identifying soft tissue abnormalities around the facial nerve.
- Evaluation of neoplasms involving the facial nerve
- Diagnosis and assessment of hemifacial spasm.
Contraindications
- Any electrically, magnetically or mechanically activated implant (e.g. cardiac pacemaker, insulin pump biostimulator, neurostimulator, cochlear implant, and hearing aids)
- Intracranial aneurysm clips (unless made of titanium)
- Pregnancy (risk vs benefit ratio to be assessed)
- Ferromagnetic surgical clips or staples
- Metallic foreign body in the eye
- Metal shrapnel or bullet
Patient preparation for Facial nerve MRI scan
- A satisfactory written consent form must be taken from the patient before entering the scanner room
- Ask the patient to remove all metal objects including keys, coins, wallet, cards with magnetic strips, jewellery, hearing aid and hairpins
- If possible provide a chaperone for claustrophobic patients (e.g. relative or staff )
- Contrast injection risk and benefits must be explained to the patient before the scan
- Gadolinium should only be given to the patient if GFR is > 30
- Offer earplugs or headphones, possibly with music for extra comfort
- Explain the procedure to the patient
- Instruct the patient to keep still
- Note the weight of the patient
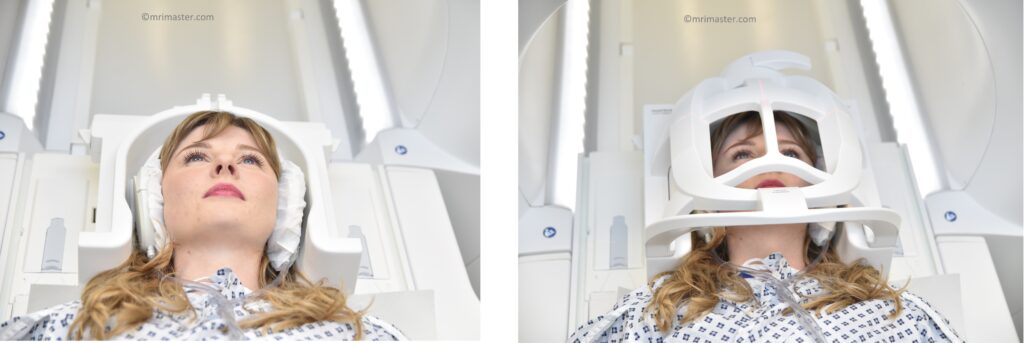
Positioning for Facial nerve MRI scan
- Head first supine
- Position the head in the head coil and immobilise with cushions
- Give cushions under the legs for extra comfort
- Centre the laser beam localizer over the glabella
Recommended Facial Nerve MRI Protocols and Planning
Facial nerve MRI localiser
To plan the sequences, it is necessary to acquire a three-plane localizer, which typically consists of T1 weighted low-resolution scans lasting less than 25 seconds.

T2 3D SPACE or CISS axial .6mm
Plan the axial slices on the sagittal plane; angle the positioning block parallel to the hard palate. Check the positioning block in the other two planes. An appropriate angle must be given in the coronal plane (perpendicular to the nasal septum). Slices must be sufficient to cover the face from the glabella down to the lower lips. If your scanner allows, consider using a small FOV 3D sequence to achieve the best results. We recommend performing these scans on a 3T scanner or a 1.5T scanner with a high-channel head coil for optimal image quality.

Parameters
TR 2000-2500 | TE 250-300 | SLICE .6MM | FLIP 150 | PHASE R>L | MATRIX 256X256 | FOV 160-180 | GAP 10% | NEX(AVRAGE) 1.6 |
T1 3D SPACE axial .9mm
Plan the axial slices on the sagittal plane; angle the positioning block parallel to the hard palate. Check the positioning block in the other two planes. An appropriate angle must be given in the coronal plane (perpendicular to the nasal septum). Slices must be sufficient to cover the face from the glabella down to the lower lips. If your scanner allows, consider using a small FOV 3D sequence to achieve the best results. We recommend performing these scans on a 3T scanner or a 1.5T scanner with a high-channel head coil for optimal image quality.

Parameters
TR 500-600 | TE 18-20 | SLICE .9MM | FLIP T1 vre | PHASE R>L | MATRIX 256X256 | FOV 170-190 | GAP 10% | NEX(AVRAGE) 2 |
T2 STIR 3D SPACE axial .9 mm
Plan the axial slices on the sagittal plane; angle the positioning block parallel to the hard palate. Check the positioning block in the other two planes. An appropriate angle must be given in the coronal plane (perpendicular to the nasal septum). Slices must be sufficient to cover the face from the glabella down to the lower lips. If your scanner allows, consider using a small FOV 3D sequence to achieve the best results. We recommend performing these scans on a 3T scanner or a 1.5T scanner with a high-channel head coil for optimal image quality.

Parameters
TR 3000-4000 | TE 250-300 | SLICE .9MM | TI 160 | PHASE R>L | MATRIX 224X224 | FOV 170-200 | GAP 10% | NEX(AVRAGE) 2 |
For contrast enhanced scans
T1 VIBE DIXON axial .6mm SFOV ISO post contrast
Plan the axial 3D block on the sagittal plane; angle the positioning block parallel to the hard palate. Check the positioning block in the other two planes. An appropriate angle must be given in the coronal plane (perpendicular to the nasal septum). Slices must be sufficient to cover the face from the glabella down to the lower lips. If your scanner allows, consider using a small FOV 3D sequence to achieve the best results. We recommend performing these scans on a 3T scanner or a 1.5T scanner with a high-channel head coil for optimal image quality.

Parameters
TR 7-8 | TE 2.39 4.77 | SLICE .6 MM | FLIP 12-15 | PHASE R>L | MATRIX 192X192 | FOV 170mm | GAP 10% | NEX(AVRAGE) 2 |
