Pediatric Brain MRI
Indications for pediatric brain MRI
- Benign and malignant tumours
- Suspected physical abuse
- Sturge-Weber syndrome
- Acute and sever headache
- Fever of unknown origin
- White matter disorders
- Vision and visual loss
- Developmental delay
- Encephalomyelitis
- Neurofibromatosis
- Vascular anomalies
- Head trauma
- Cavernomas
- Optic neuritis
- Encephalitis
- Meningitis
- Vasculitis
- Cerebritis
- Empyema
- Seizures
- Abscess
- Ataxia
Contraindications
- Any electrically, magnetically or mechanically activated implant (e.g. cardiac pacemaker, insulin pump biostimulator, neurostimulator, cochlear implant, and hearing aids)
- Intracranial aneurysm clips (unless made of titanium)
- Ferromagnetic surgical clips or staples
- Metallic foreign body in the eye
- Metal shrapnel or bullet
Patient preparation
- A satisfactory written consent form must be taken from the patient before entering the scanner room (For paediatric patients this must be done by the parents)
- Ask the patient to remove all metal objects including keys, coins, wallet, cards with magnetic strips, jewellery, hearing aid and hairpins
- Provide a chaperone for claustrophobic patients (e.g. parents or staff )
- Contrast injection risk and benefits must be explained to the before the scan
- Offer earplugs or headphones, possibly with music for extra comfort
- Explain the procedure to the patient
- Instruct the patient to keep still
- Note the hight and weight of the patient
Patient preparation for under 3 and neonates
- Please do necessary arrangements for sedation if prescribed (oral chloral hydrate used for this purpose)
- Infants must be Fed immediately before the scan and wrap them in a warm blanket (must be done by a trained nurse).
- Room temperature must be maintained (23-24 degrees for term born infants and approx. 28 degrees for preterm infants)
- Change nappies immediately before the procedure
- If available use the acoustic noise reduction sequences
- All the ECG electrodes must be removed prior to procedure
- Sedated patients must be monitor (using MRI compactable pulse oximeter)
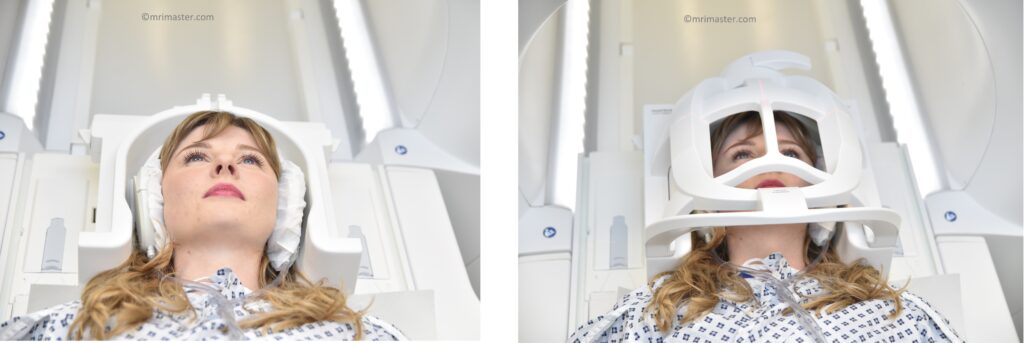
Positioning
- Head first supine
- Position the head in the head coil and immobilise with cushions
- Cover the baby with blanket and immobilize with straps
- Centre the laser beam localiser over the glabella
pediatric brain mri Protocols, Parameters, and Planning
localiser
A three-plane localizer must be taken at the beginning to localize and plan the sequences. Localizers are usually less than 25 seconds and are T1-weighted low-resolution scans.

T2+PD Duel echo
Plan the axial slices on the sagittal plane and position the block parallel to the genu and splenium of the corpus callosum. Verify the planning block in the other two planes and ensure that an appropriate angle is maintained in the coronal plane, making it perpendicular to the line of the midline of the brain and the 4th ventricle. Ensure that the number of slices is sufficient to cover the entire brain from the vertex to the line of the foramen magnum.

Parameters
TR 3000-4000 | TE T2 100-120 PD 15-20 | SLICE 3MM | FLIP 130-150 | PHASE R>L | MATRIX 256X256 | FOV 150-190 | GAP 10% | NEX(AVRAGE) 2 |
What are the reasons for conducting PD + T2 dual echo scans in pediatric brain MRI?
Performing PD + T2 dual echo scans in pediatric brain MRI offers valuable advantages. Firstly, it improves tissue contrast by utilizing the complementary information provided by PD and T2-weighted images. PD-weighted images excel at differentiating between gray and white matter, while T2-weighted images are excellent for visualizing pathological conditions like edema, tumors, and ischemic lesions. By combining these sequences, the overall tissue contrast is enhanced, leading to improved diagnostic accuracy.
Secondly, dual echo scans aid in lesion detection. Certain brain abnormalities, such as specific tumors or white matter lesions, may be more pronounced on PD-weighted images, whereas cysts or fluid-filled structures are better visualized on T2-weighted images. Simultaneously acquiring both sequences increases the likelihood of detecting a broader range of lesions, thereby enhancing diagnostic confidence.
T1 TSE axial small fov 3mm
Plan the axial slices on the sagittal plane and position the block parallel to the genu and splenium of the corpus callosum. Verify the planning block in the other two planes and ensure that an appropriate angle is maintained in the coronal plane, making it perpendicular to the line of the midline of the brain and the 4th ventricle. Ensure that the number of slices is sufficient to cover the entire brain from the vertex to the line of the foramen magnum.

Parameters
TR 400-600 | TE 15-25 | SLICE 3MM | FLIP 140 | PHASE R>L | MATRIX 256X256 | FOV 150-190 | GAP 10% | NEX(AVRAGE) 2 |
T2 flair coronal 3mm small fov
Plan the coronal slices on the sagittal plane and angle the positioning block perpendicular to the line along the genu and splenium of the corpus callosum. Verify the planning block in the other two planes. Ensure that an appropriate angle is maintained in the axial plane, perpendicular to the midline of the brain. The number of slices should be sufficient to cover the entire brain from the frontal sinus to the line of the occipital protuberance.

Parameters
TR 7000-9000 | TE 110 | FLIP 130 | NEX 2 | SLICE 3 MM | MATRIX 256X256 | FOV 150-190 | PHASE R>L | GAP 10% | TI 2500 |
T1 SPACE 3D sagittal 3mm
Plan the sagittal 3D block on the axial plane and position the block parallel to the midline of the brain. Verify the planning block in the other two planes. Angle the positioning block appropriately in the coronal plane, ensuring it is parallel to the line along the midline of the brain and the 4th ventricle. Make sure that the number of slices is sufficient to cover the entire brain from one temporal lobe to the other. To prevent wrap-around artifacts, both phase oversampling and slice oversampling must be used.

Parameters
TR 680 | TE 11-12 | SLICE 1MM | FLIP T1 ver | PHASE A>P | MATRIX 256X256 | FOV 180-200 | IPAT CS | NEX(AVRAGE) 1 |
Why T1 3D imaging is useful in pediatric brain imaging
T1 3D imaging allows for excellent visualization of the brain structures in their natural orientation. It provides detailed information about the size, shape, and location of various brain regions, which is essential for evaluating structural abnormalities that may contribute to seizures.
T2 TSE sagittal 3mm SFOV
Plan the sagittal slices on the axial plane and position the block parallel to the midline of the brain. Verify the planning block in the other two planes. Angle the positioning block appropriately in the coronal plane, ensuring it is parallel to the line along the midline of the brain and the 4th ventricle. Make sure that the number of slices is sufficient to cover the entire brain from one temporal lobe to the other.

Parameters
TR 4500-6000 | TE 100-120 | SLICE 3MM | FLIP 130-150 | PHASE A>P | MATRIX 288X288 | FOV 150-190 | GAP 10% | NEX(AVRAGE) 2 |
RESOLVE DWI AXIAL 3mm
Plan the axial slices on the sagittal plane and position the block parallel to the genu and splenium of the corpus callosum. Verify the planning block in the other two planes and ensure that an appropriate angle is maintained in the coronal plane, making it perpendicular to the line of the midline of the brain and the 4th ventricle. Ensure that the number of slices is sufficient to cover the entire brain from the vertex to the line of the foramen magnum.

Parameters
TR 7000-9000 | TE 70 | FLIP 130 | NXA 1 2 | SLICE 3MM | MATRIX 192X192 | FOV 210-230 | PHASE R>L | GAP 10% | B VALUE 0 |
Optional Scans
T1 SPACE 3D axial small fov 1 mm isotropic
Plan the axial 3D block on the sagittal plane and position the block parallel to the genu and splenium of the corpus callosum. Verify the planning block in the other two planes and ensure that an appropriate angle is maintained in the coronal plane, making it perpendicular to the line of the midline of the brain and the 4th ventricle. Ensure that the number of slices is sufficient to cover the entire brain from the vertex to the line of the foramen magnum. To prevent wrap-around artifacts, both phase oversampling and slice oversampling must be used.

Parameters
TR 680 | TE 11-12 | SLICE 1MM | FLIP T1 ver | PHASE A>P | MATRIX 256X256 | FOV 180-200 | IPAT CS | NEX(AVRAGE) 1 |
T1 SPACE 3D coronal small fov 1 mm isotropic
Plan the coronal 3D block on the sagittal plane and angle the positioning block perpendicular to the line along the genu and splenium of the corpus callosum. Verify the planning block in the other two planes. Ensure that an appropriate angle is maintained in the axial plane, perpendicular to the midline of the brain. The number of slices should be sufficient to cover the entire brain from the frontal sinus to the line of the occipital protuberance.

Parameters
TR 680 | TE 11-12 | SLICE 1MM | FLIP T1 ver | PHASE A>P | MATRIX 256X256 | FOV 180-200 | IPAT CS | NEX(AVRAGE) 1 |
Indications for contrast enhancement brain scans
- Tumour, Metastasis, Cranial nerve lesion, Indeterminate intracranial lesion, internal auditory canal mass
- Meningitis, Encephalitis, Leptomeningeal spread
- AVM and Infection Abscess
- Leukodystrophies, Delayed development
- Syringomyelia(Syrinx)


