MRI Iliopsoas Bursitis
Iliopsoas bursitis, also known as iliopectineal bursitis, is an inflammatory condition involving the iliopsoas bursa, a fluid-filled sac located in the pelvic region. This bursa acts as a cushion, reducing friction between the iliopsoas muscle and the pelvis or hip bone. Inflammation of this bursa can lead to pain and discomfort, often associated with hip and groin region.
Causes:
Overuse or Repetitive Stress: Common in athletes, especially runners, or individuals involved in activities requiring repetitive hip flexion.
Hip Injury or Trauma: Direct injury to the hip area can lead to inflammation of the bursa.
Arthritis: Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or osteoarthritis can precipitate iliopsoas bursitis.
Leg Length Discrepancy: Uneven leg lengths can cause abnormal gait, leading to extra stress on the bursa.
Symptoms:
Pain: Often the most prominent symptom, typically felt in the front of the hip, but it can also radiate to the thigh, groin, or lower back.
Swelling: May occur in the affected area.
Tenderness: The area over the bursa may be tender to touch.
Stiffness: The hip might feel stiff, especially after prolonged sitting or in the morning.
Reduced Range of Motion: Movement of the hip, particularly hip flexion, may become limited.
Treatment:
Rest: Reducing activities that exacerbate the symptoms is crucial.
Ice Therapy: Applying ice to the affected area can help reduce inflammation and pain.
Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Medications like ibuprofen or naproxen can help in reducing pain and inflammation.
Physical Therapy: Guided exercises to strengthen the surrounding muscles, improve flexibility, and correct any biomechanical issues.
Corticosteroid Injections: These can be administered into the bursa to reduce inflammation and pain, though their use may be limited due to potential side effects.
Surgery: In rare cases where conservative treatments fail, surgical intervention to remove the inflamed bursa may be considered.
MRI Appearance of Iliopsoas Bursitis
T1-Weighted Images:
- In T1-weighted images, fluid within the bursa, which is indicative of bursitis, typically appears as low signal intensity (dark) compared to surrounding structures.
- The iliopsoas muscle and tendon appear as intermediate to low signal intensity.
T2-Weighted Images:
- On T2-weighted images, fluid within the bursa appears as high signal intensity (brighter), which is indicative of inflammation or fluid accumulation.
- These images are particularly useful for detecting edema and inflammation.
STIR (Short Tau Inversion Recovery):
- STIR is a fluid-sensitive sequence that suppresses fat signal, making fluid appear very bright. This is very sensitive for detecting edema or inflammation.
- Iliopsoas bursitis will show as increased signal intensity (brighter areas) in the region of the bursa.
PD (Proton Density) Fat Saturation:
- This sequence also helps in detecting fluid and edema. The fat saturation component suppresses the signal from fat, making it easier to view edema or fluid.
- The inflamed bursa would appear as an area of increased signal intensity (brightness) compared to the surrounding structure
T2 TSE sagittal image shows Iliopsoas Bursitis

STIR coronal image shows Iliopsoas Bursitis

T1 coronal image shows Iliopsoas Bursitis
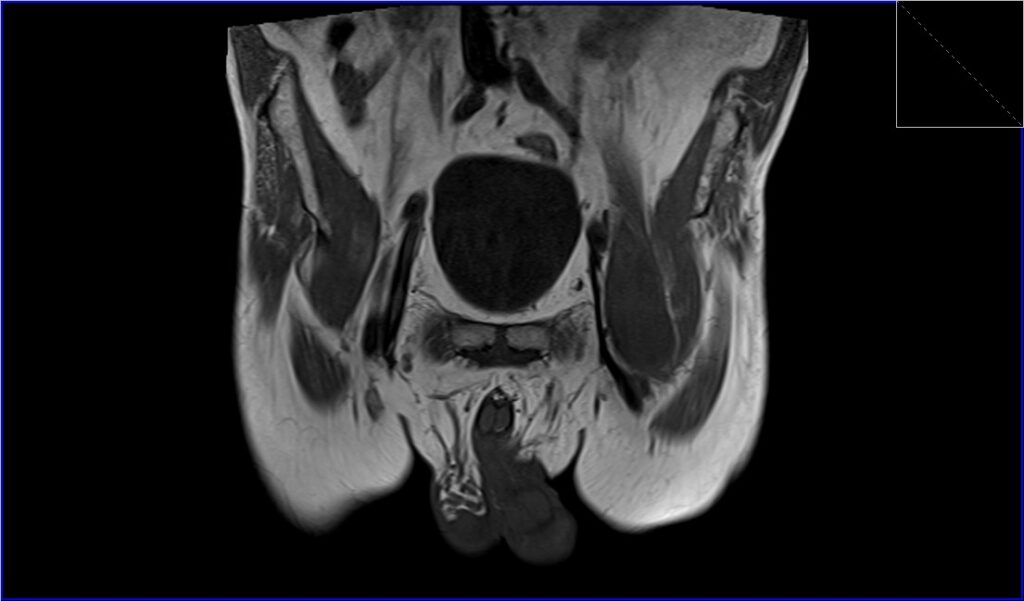
STIR axial image shows Iliopsoas Bursitis

T1 axial image shows Iliopsoas Bursitis

References
- Skiadas, V., Koutoulidis, V., & Plotas, A. (2009). An atypical case of noninfected iliopsoas bursitis – MRI findings. J Radiol Case Rep, 3(10), 15–18. doi:10.3941/jrcr.v3i10.326
- Corvino, A., Venetucci, P., Caruso, M., Tarulli, F. R., Carpiniello, M., Pane, F., Sabatino, V., Franzese, R., Catalano, O., Corvino, F., & Catelli, A. (2020). Iliopsoas bursitis: The role of diagnostic imaging in detection, differential diagnosis, and treatment. Radiology Case Reports, 15(11), 2149-2152.
- Varma, D. G. K., Richli, W. R., Charnsangavej, C., Samuels, B. I., Kim, E. E., & Wallace, S. (1991). MR Appearance of the Distended Iliopsoas Bursa. AJR, 156(5), 1025-1028. doi:10.2214/ajr.156.5.201025
- Wunderbaldinger, P., Bremer, C., Schellenberger, E., Cejna, M., Turetschek, K., & Kainberger, F. (2002). Imaging features of iliopsoas bursitis. European Radiology, 12(2002), 409-415.


