Iliofemoral deep vein thrombosis (DVT) MRI
Iliofemoral deep vein thrombosis (DVT) refers to the formation of a blood clot in the deep veins of the iliofemoral region, which includes the iliac veins and the femoral veins in the pelvis and upper thigh. This condition is serious and can lead to significant complications if not treated promptly.
Causes
Iliofemoral DVT can be caused by several factors, including:
- Prolonged Immobilization: Long periods of inactivity, such as bed rest or long flights.
- Surgery and Trauma: Especially orthopedic surgeries or trauma to the legs.
- Cancer: Certain cancers can increase the risk of clot formation.
- Hormonal Factors: Pregnancy, birth control pills, or hormone replacement therapy.
- Obesity: Increased body weight can put more pressure on veins.
- Other Medical Conditions: Heart failure, inflammatory bowel disease, and nephrotic syndrome.
Symptoms
Symptoms of iliofemoral DVT can include:
- Swelling: Typically in the thigh or lower leg.
- Pain: A deep, aching pain in the affected area.
- Redness and Warmth: The skin over the affected area may appear red and feel warm.
- Tenderness: The area may be tender to the touch.
- Leg Fatigue: The affected leg may feel tired or heavy.
- Visible Veins: Surface veins may become more prominent.
Diagnosis
- Clinical Examination: Initial assessment based on symptoms and physical examination.
- Ultrasound: Doppler ultrasound is the primary imaging modality used to visualize blood flow and detect clots.
- MRI or CT Scan: These imaging techniques may be used to get a clearer view of the veins
Treatment
- Anticoagulation Therapy: Mainstay of treatment to prevent further clotting and reduce the risk of complications. Common medications include heparin, warfarin, and newer direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs).
- Thrombolysis: In cases of severe DVT, thrombolytic therapy may be used to dissolve the clot. This involves injecting clot-dissolving medications directly into the vein.
- Compression Stockings: Used to reduce swelling and prevent post-thrombotic syndrome, a long-term complication of DVT.
- Surgical Intervention: In rare and severe cases, surgical removal of the clot (thrombectomy) may be necessary.
- Inferior Vena Cava (IVC) Filter: A filter may be placed in the inferior vena cava to prevent clots from traveling to the lungs in patients who cannot take
MRI Appearance of Iliofemoral Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
TOF 2D MRV Appearance
Time-of-Flight (TOF) 2D Magnetic Resonance Venography (MRV) is a non-contrast technique that is particularly useful in visualizing the venous system. In cases of iliofemoral DVT, TOF MRV will show an absence of flow-related enhancement in the affected vein, indicating the presence of a thrombus. The thrombus appears as a signal void or low signal intensity region within the vein, which contrasts with the bright signal of the flowing blood in unobstructed segments. This technique is valuable for mapping the extent of the thrombus and assessing the patency of the venous system.
MRI T1 Appearance
On MRI T1-weighted images, iliofemoral deep vein thrombosis (DVT) typically presents as a region of intermediate to low signal intensity within the lumen of the affected vein. This appearance is due to the presence of acute thrombus, which has a composition similar to blood but lacks flow, resulting in signal characteristics that are distinguishable from the surrounding tissues. Chronic DVT may also show low signal intensity on T1-weighted images due to fibrosis and recanalization within the thrombus.
MRI T2 Appearance
On MRI T2-weighted images, iliofemoral DVT appears as an area of high signal intensity within the vein. This is due to the higher water content of the thrombus in the acute and subacute phases. The high signal is more conspicuous against the low signal of the blood flow in adjacent veins. In chronic DVT, the signal may vary, showing mixed intensity due to the presence of organized thrombus and fibrotic tissue.
Post-contrast T1 with Fat Saturation (T1 FS) Appearance
Post-contrast T1-weighted images with fat saturation (T1 FS) enhance the detection of iliofemoral DVT by providing clear delineation of the thrombus against the enhancing vessel walls and surrounding tissues. The thrombus itself typically does not enhance, appearing as a filling defect within the enhancing lumen of the vein. Fat saturation improves the contrast between the thrombus and surrounding fat, aiding in the identification of the extent and morphology of the thrombus.
TOF 2D axial image shows Iliofemoral Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)






Coronal MRI of TOF 2D axial image shows Iliofemoral Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
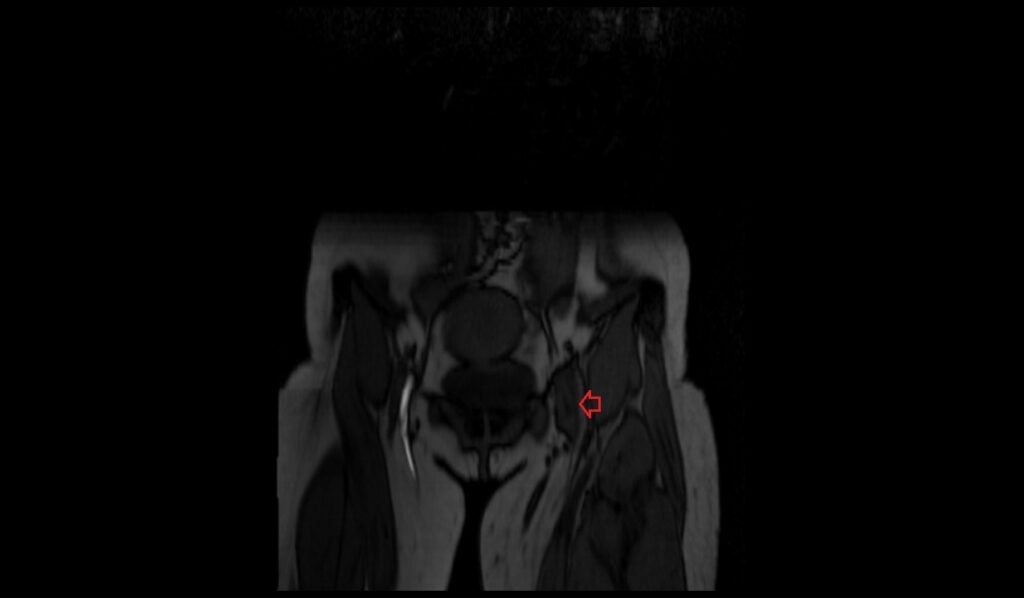
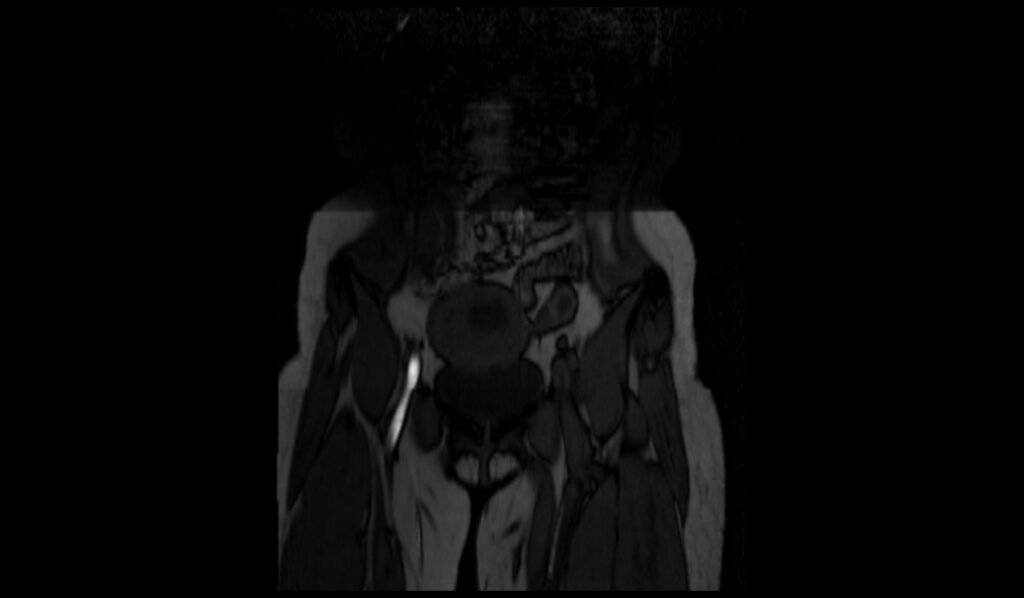
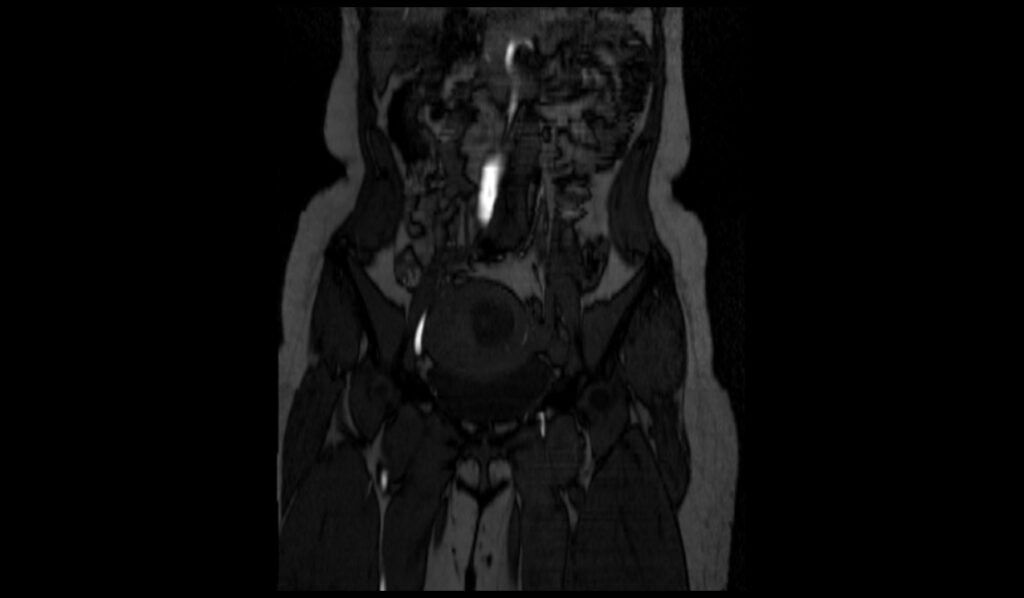

T1 FS axial image shows Iliofemoral Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)





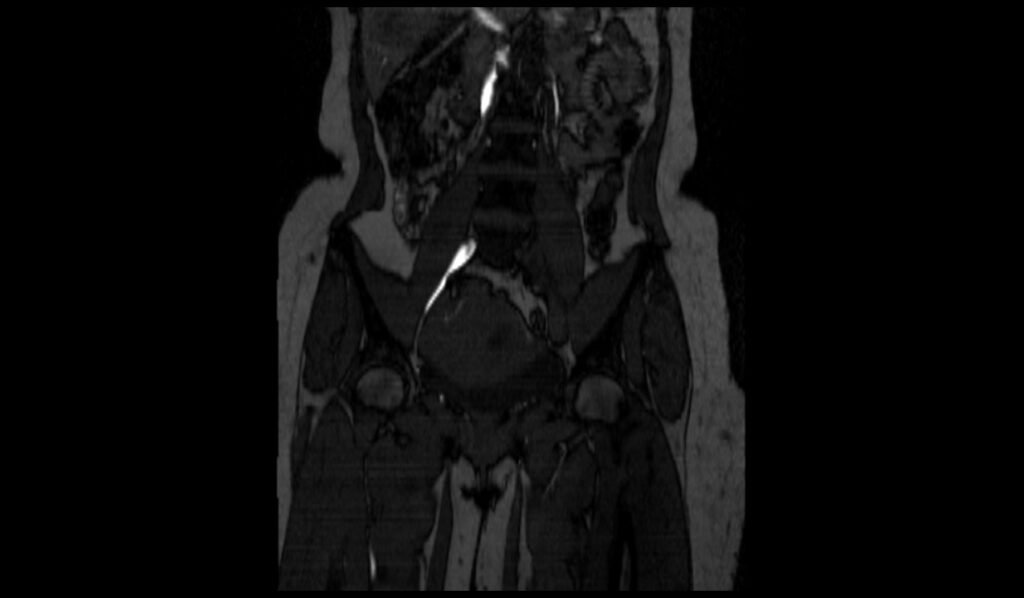
TOF 2D MIP image shows Iliofemoral Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)


References
- Liu, D., Peterson, E., Dooner, J., Baerlocher, M., Zypchen, L., Gagnon, J., Delorme, M., Kim Sing, C., Wong, J., Guzman, R., Greenfield, G., Moodley, O., & Yenson, P., for the Interdisciplinary Expert Panel on Iliofemoral Deep Vein Thrombosis (InterEPID). (2015). Diagnosis and management of iliofemoral deep vein thrombosis: clinical practice guideline. CMAJ, 187(17), 1288–1296. https://doi.org/10.1503/cmaj.141614
- Dronkers, C. E. A., Srábek, A., Huisman, M. V., & Klok, F. A. (2016). Accurate diagnosis of iliac vein thrombosis in pregnancy with magnetic resonance direct thrombus imaging (MRDTI). BMJ Case Reports, 2016, bcr2016218091. https://doi.org/10.1136/bcr-2016-218091
- Lyhne, L.; Houlind, K.C.; Christensen, J.; Vijdea, R.L.; Hansen, M.R.; Pedersen, M.R.V.; Precht, H. Magnetic Resonance Imaging as a Diagnostic Tool for Ilio-Femoro-Caval Deep Venous Thrombosis. J. Imaging 2024, 10, 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging10030066


