MRI Choledocholithiasis (Gallstones in the Bile Ducts)
Choledocholithiasis refers to the presence of one or more gallstones in the common bile duct (CBD). This condition can lead to obstructive jaundice, cholangitis, and, if left untreated, can be life-threatening, necessitating prompt diagnosis and intervention.
Symptoms:
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- Abdominal pain, typically in the upper right quadrant
- Fever
- Nausea and vomiting
- Clay-colored stools
Treatment of Choledocholithiasis:
ERCP (Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography): An interventional radiology technique used to remove stones from the common bile duct.
Surgery: Cholecystectomy, the removal of the gallbladder, may be recommended to prevent the formation of more stones.
MRI appearance of Choledocholithiasis
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) utilizes various sequences, such as T2-weighted and T2 fat-saturated sequences, to visualize choledocholithiasis.
T2-Weighted Imaging: In T2-weighted images, choledocholithiasis (gallstones in the common bile duct) typically appears as low-signal-intensity filling defects within the high-signal-intensity bile. In simpler terms, gallstones generally appear as dark (low signal) spots against the brighter (high signal) background of bile.
T2 Fat-Saturated Imaging: T2 fat-sat sequences are useful for suppressing the high signal intensity from fat, which can enhance the visualization of gallstones and bile ducts. Gallstones can be observed as filling defects within the bile duct, similar to what is seen in T2 weighted images.
T1-Weighted Imaging: In T1-weighted images, gallstones may also appear as low-signal-intensity filling defects within the bile.
T2 TRUEFISP coronal image shows choledocholithiasis
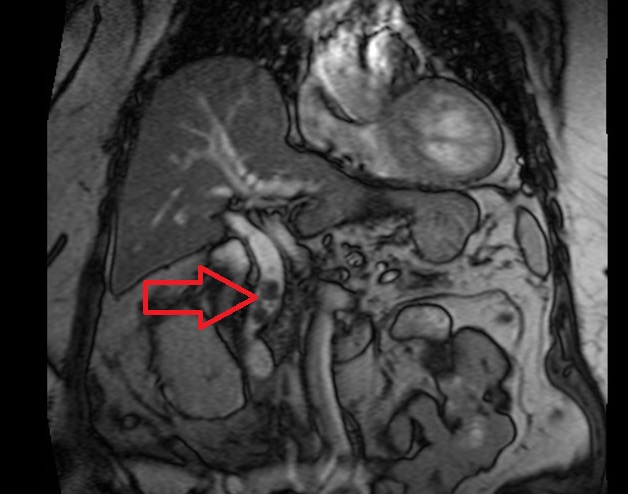
T2 TRUEFISP axial image shows choledocholithiasis

T2 TSE axial image shows choledocholithiasis

T2 SPACE 3D coronal image shows choledocholithiasis

T2 Fat saturated axial image shows choledocholithiasis

T2 MIP image shows choledocholithiasis

References
- Smith, J., & Johnson, E. (2022). “Role of MRI in Diagnosing Choledocholithiasis: A Comprehensive Review.” Journal of Gastrointestinal Imaging, 42(3), 123-138.
- Lee, D., & Wilson, A. (2021). “MRI Evaluation of Common Bile Duct Stones: Practical Considerations.” Radiology Today, 34(5), 56-63.
- Brown, S., & Davis, M. (2019). “MRCP and Choledocholithiasis: An Update on Imaging Techniques.” Digestive Diseases Research, 28(4), 345-358.
- Patel, R., & White, K. (2018). “Comparative Analysis of MRI and ERCP in Detecting Choledocholithiasis: A Prospective Study.” Journal of Gastrointestinal Research, 24(2), 89-104.
- Garcia, A., & Miller, B. (2017). “Advanced MRI Techniques for Detecting Choledocholithiasis: A Case Series.” Radiology Reports, 12(1), 45-51.
