MRI Deep Resolve
Deep Resolve
Deep Resolve MRI is an advanced medical imaging technology that combines deep learning and artificial intelligence (AI) techniques to enhance the process of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) image reconstruction. It encompasses several components, including Deep Resolve Gain, Deep Resolve Sharp, Deep Resolve Boost, and Deep Resolve Swift Brain.
Deep Resolve Gain: Deep Resolve Gain is an advanced denoising solution that enhances the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) in MRI scans by addressing spatially varying noise. This variation often arises from factors like coil array geometries and parallel imaging reconstruction techniques. Unlike traditional global noise filters, Deep Resolve Gain generates specific noise maps from the raw MRI data, reflecting local noise distributions. These maps are integrated into an iterative reconstruction process, allowing for targeted denoising—applying stronger noise reduction in areas where noise is most prominent. This approach enables higher acceleration factors without compromising image quality .
T2 TSE image without deep resolve
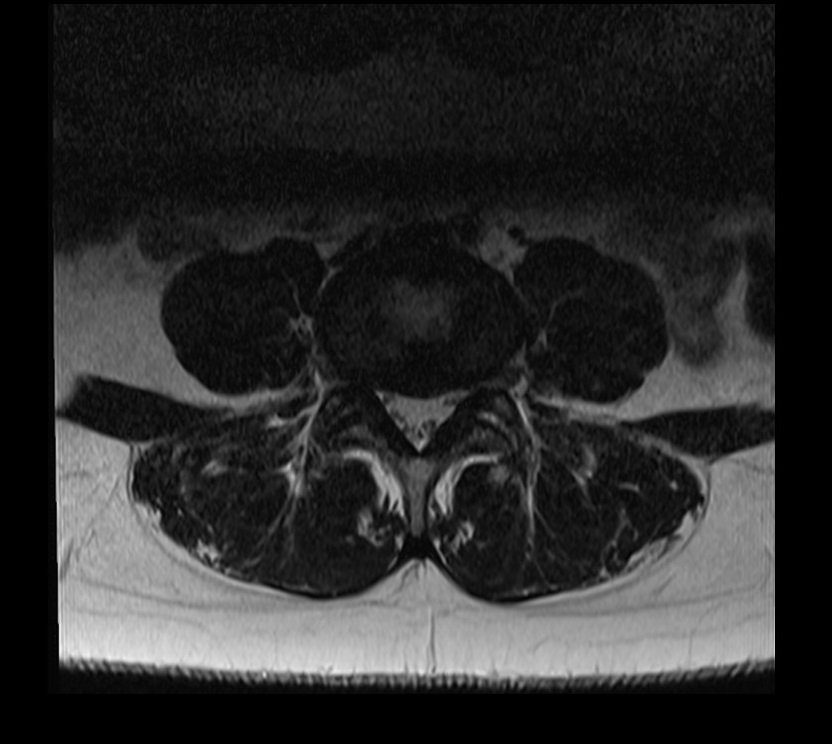
Matrix size 224x224 and NEX 1 scantime : 1.20minutes
Deep Resolve Gain
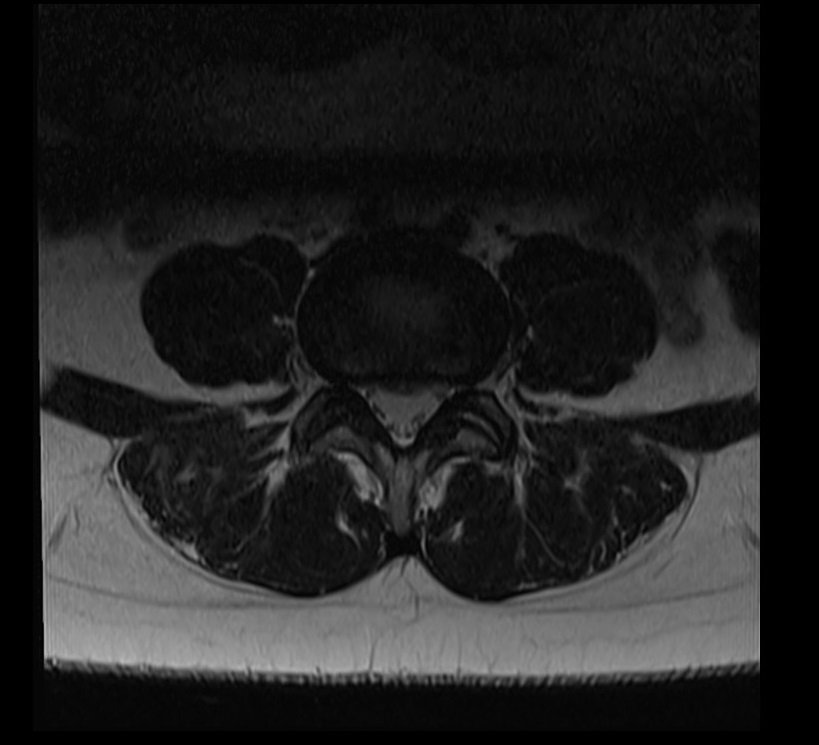
Matrix size 224x224 and NEX 1 scantime : 1.20minutes
Deep Resolve Sharp: Deep Resolve Sharp is an AI-powered image reconstruction technology designed to enhance image sharpness. It employs a deep neural network trained on extensive datasets comprising low- and high-resolution image pairs. During reconstruction, the network predicts high-resolution details from low-resolution input, effectively increasing the in-plane matrix size by up to a factor of two along each axis. Crucially, the acquired raw data remains integral to the reconstruction process, ensuring consistency and preserving image contrast .
T2 TSE image without deep resolve
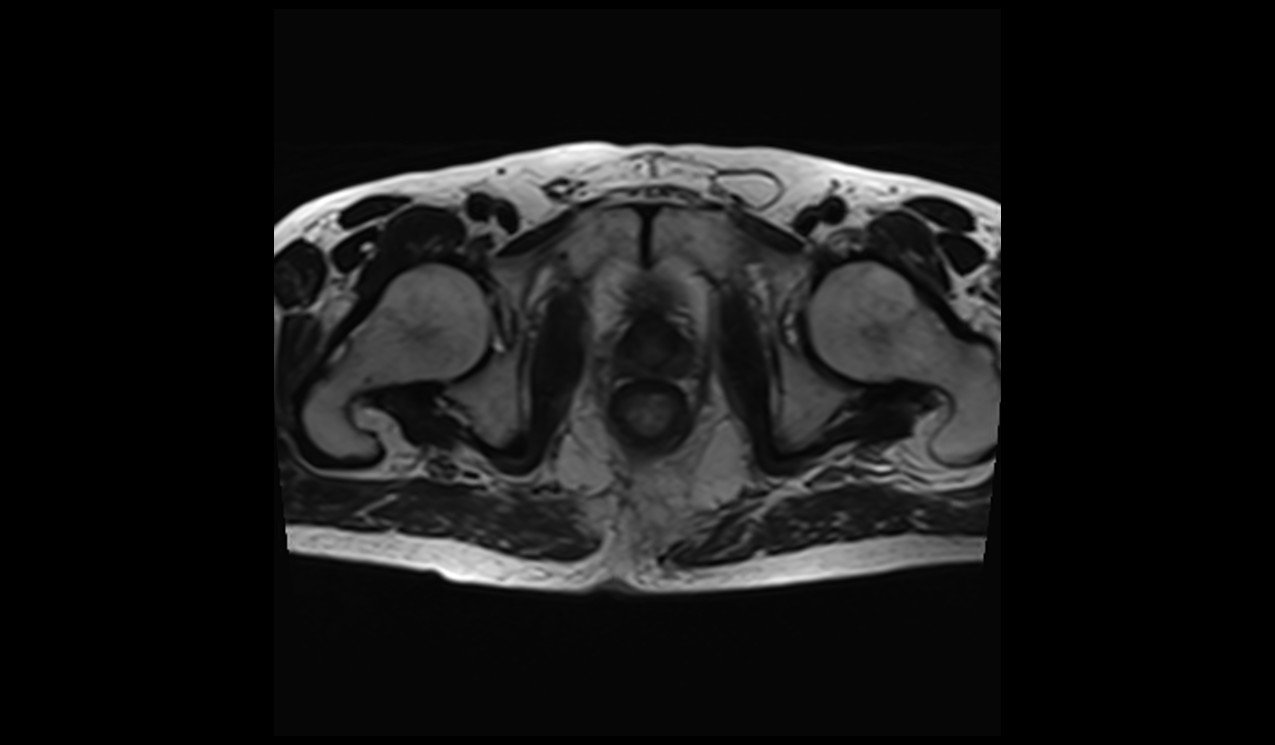
Matrix size 192x192 and NEX 1 scantime : 1.30minutes
Deep Resolve Gain + Sharp
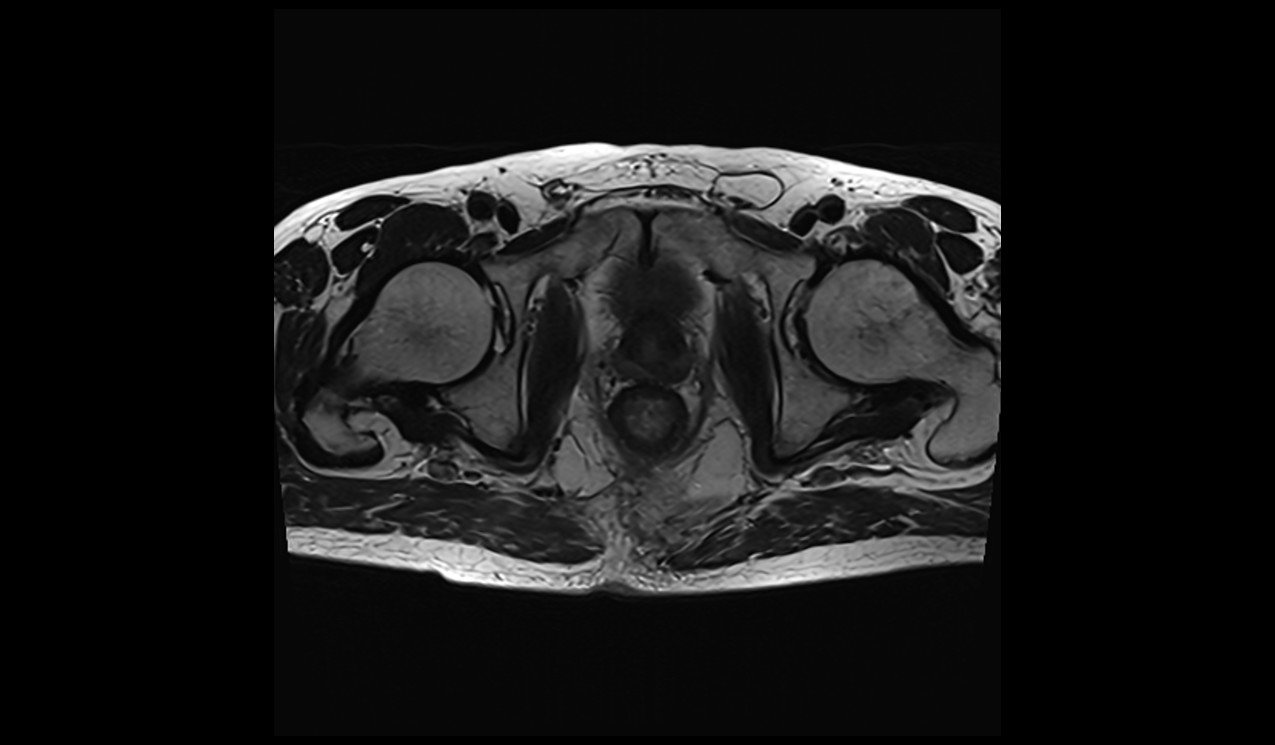
Matrix size 192X192 and NEX 1 scantime : 1.30minutes
Deep Resolve Boost: Deep Resolve Boost is a raw-data-to-image deep learning reconstruction technology that significantly accelerates MRI acquisition while maintaining high image quality. By applying deep neural networks directly to the raw data, it enables substantial scan time reductions—for instance, completing a total knee exam in under two minutes—without compromising resolution. Deep Resolve Boost is applicable across various anatomical regions and can be combined with Siemens Healthineers’ Simultaneous Multi-Slice (SMS) technique for even greater acceleration .
T2 TSE image without deep resolve
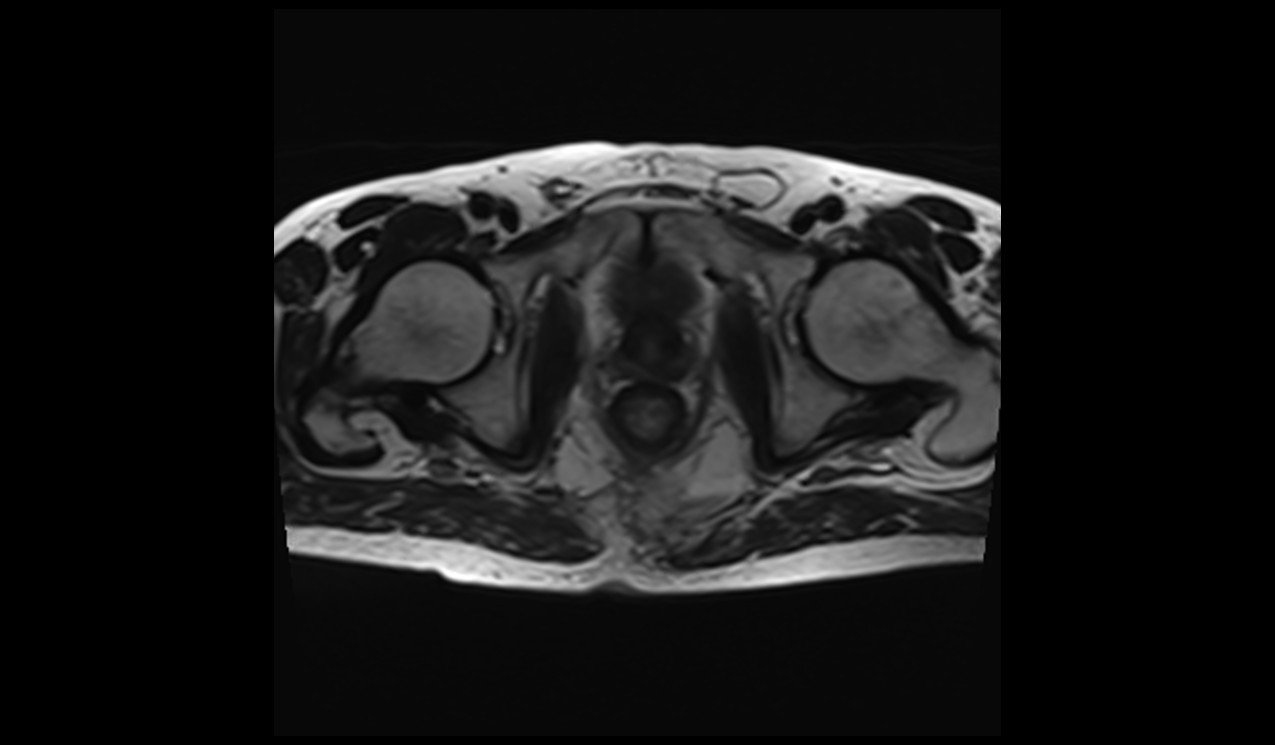
Matrix size 192X192 and NEX 1 scantime : 1minute
Deep Resolve Boost
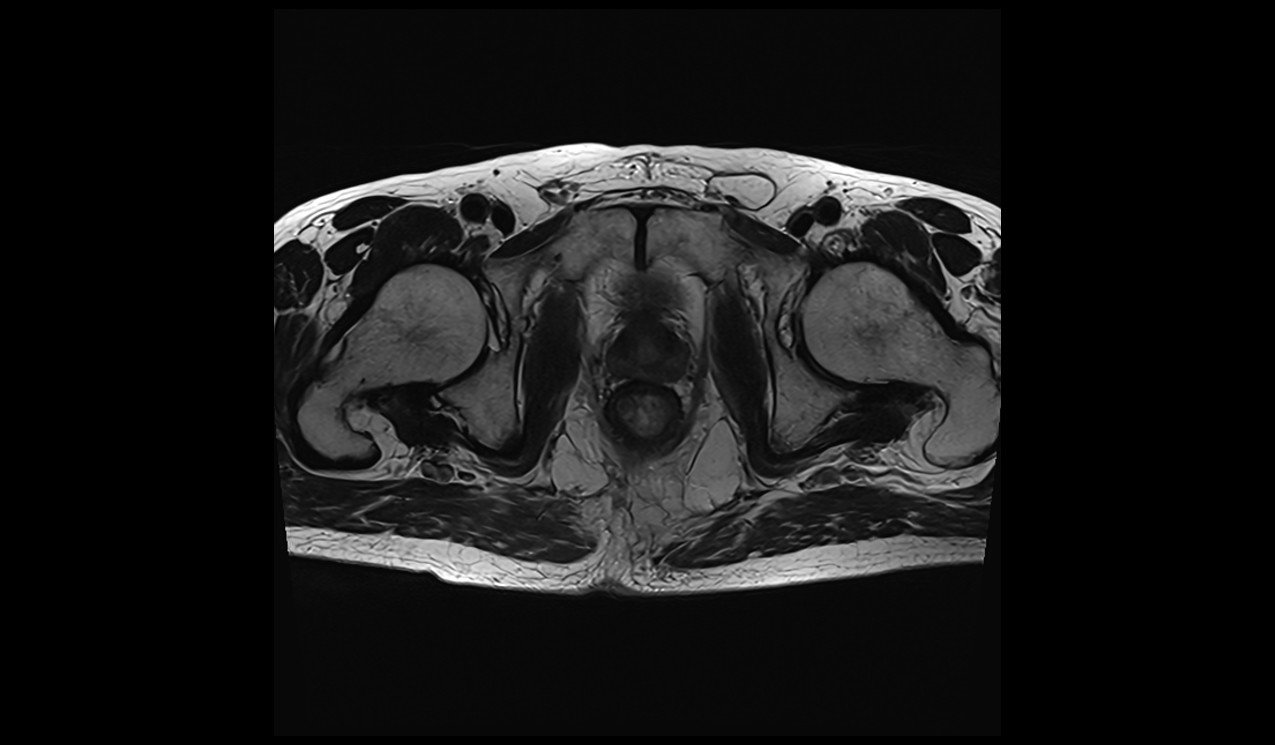
Matrix size 192X192 and NEX 1 scantime : 1minute
Advantages of Deep Resolve MRI
Improved Image Quality: Deep Resolve Gain reduces noise and enhances image clarity, while Deep Resolve Sharp increases image sharpness, resulting in better diagnostic accuracy.
Faster Scan Times: Deep Resolve Boost accelerates image acquisition without compromising signal-to-noise ratio, reducing patient discomfort and enhancing workflow efficiency.
T2 TSE image without deep resolve
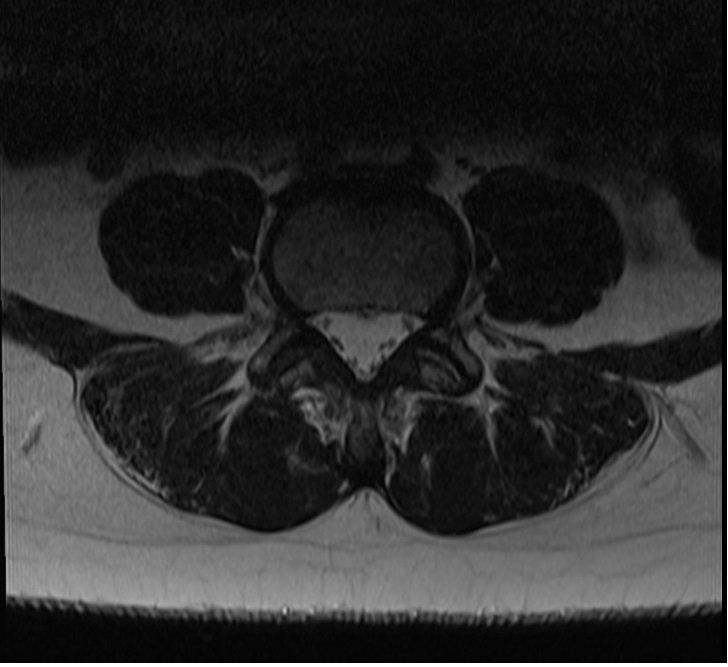
Matrix size 256X256, NEX 2 and IPAT: OFF | scantime : 2.10minutes
Deep Resolve Boost
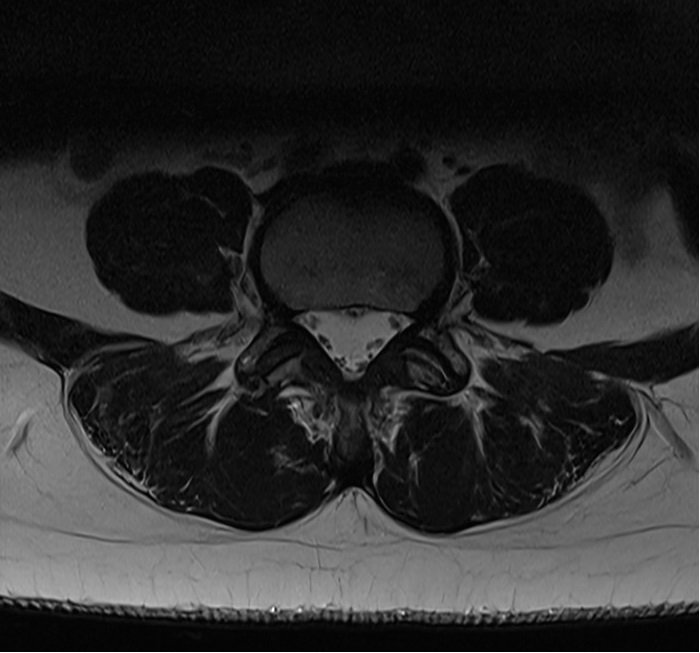
Matrix size 240X240, NEX 1 and IPAT: GRAPPA 2 | scantime : 1.05minute
Artifacts Associated with Deep Resolve MRI
Noise Artifacts: While Deep Resolve Gain reduces noise, improper handling of noise maps may lead to residual noise artifacts in the reconstructed images.
Sharpness Artifacts: Deep Resolve Sharp’s focus on increasing sharpness may lead to accentuated high-frequency noise or unrealistic edge enhancements.
Motion Artifacts: Rapid image acquisition enabled by Deep Resolve Boost and Swift Brain may be susceptible to motion artifacts in patients who struggle to remain still.
Aliasing Artifacts: There are situations where the Deep Resolve algorithms may encounter difficulty accurately portraying intricate anatomical formations, potentially resulting in distortions or the emergence of aliasing artifacts. The occurrence of aliasing artifacts tends to be more frequent in areas demanding substantial oversampling, such as in the sagittal view of the spine, for instance.
Deep Resolve Gain Sharpness Artifacts
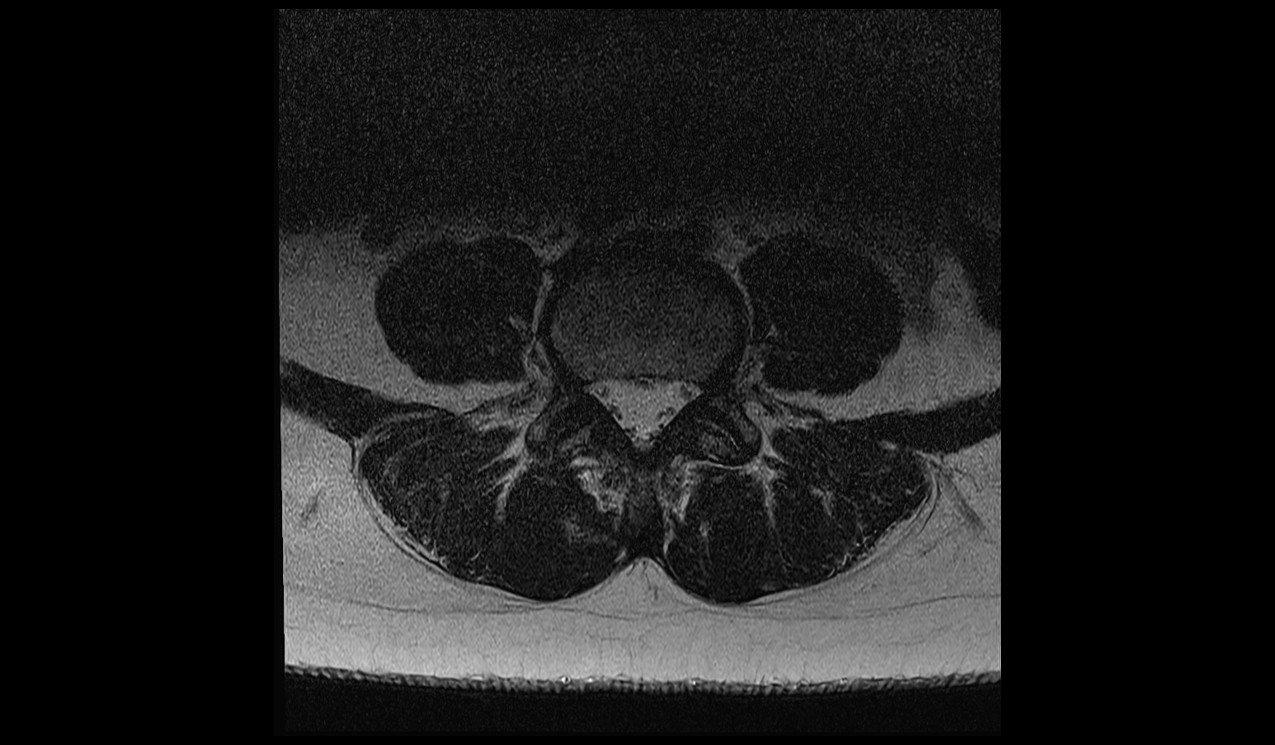
Deep Resolve Gain Sharpness Artifacts
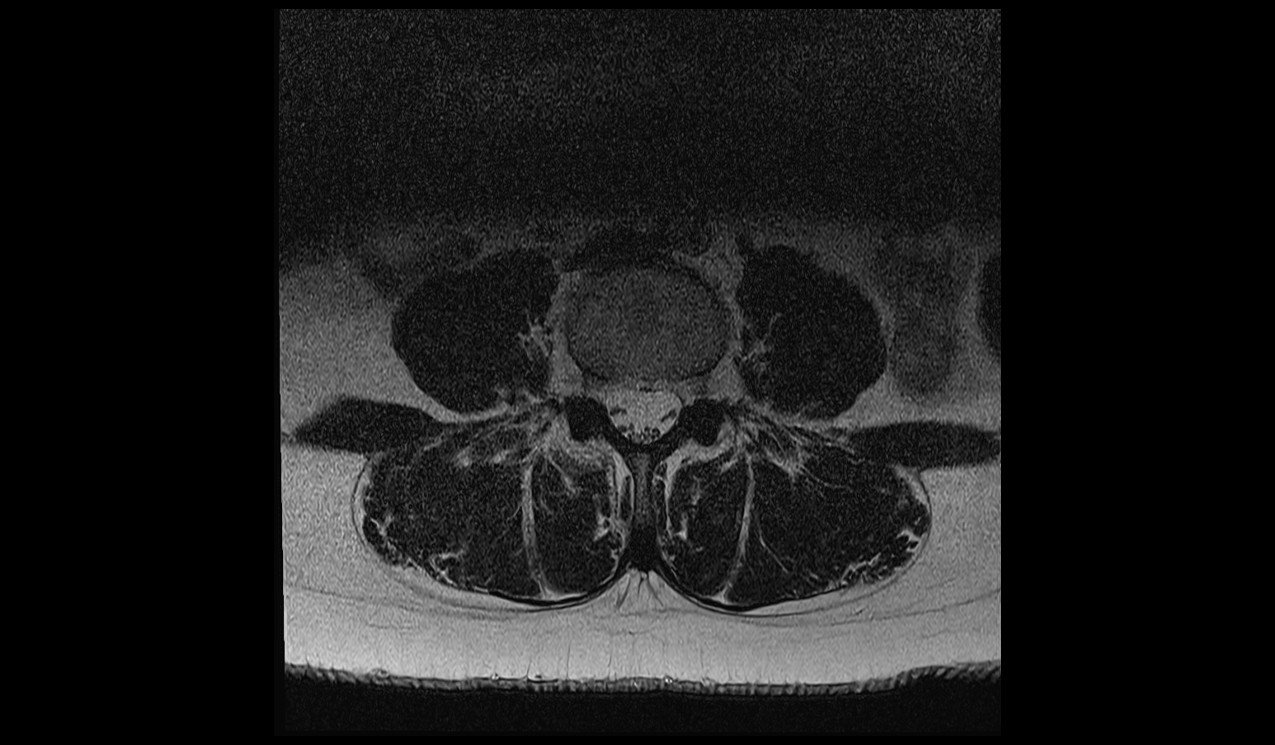
Deep Resolve Boost aliasing Artifacts

Deep Resolve Boost enhances motion artifact
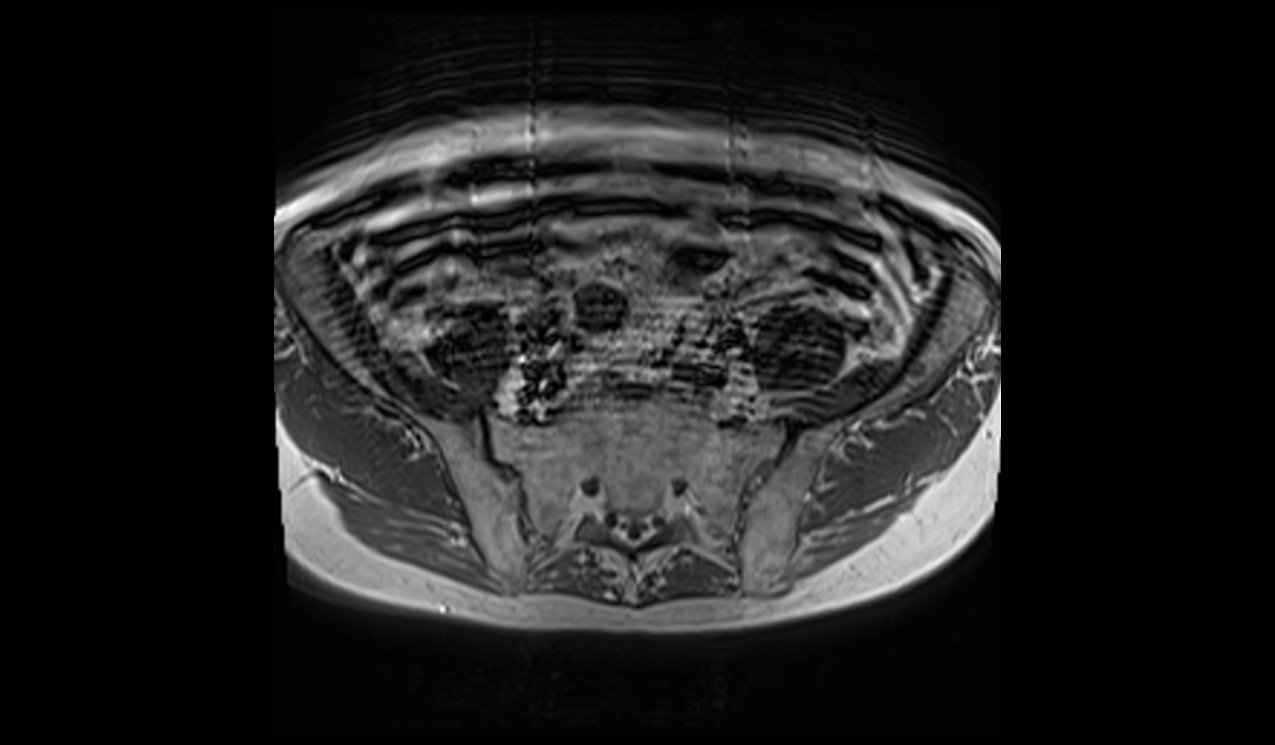
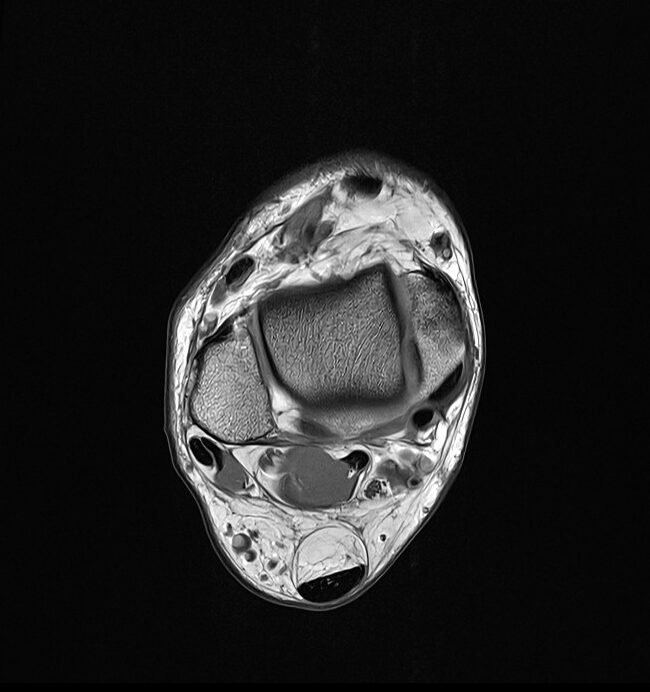
An unknown artifact was produced by Deep Resolve Boost with a high matrix size
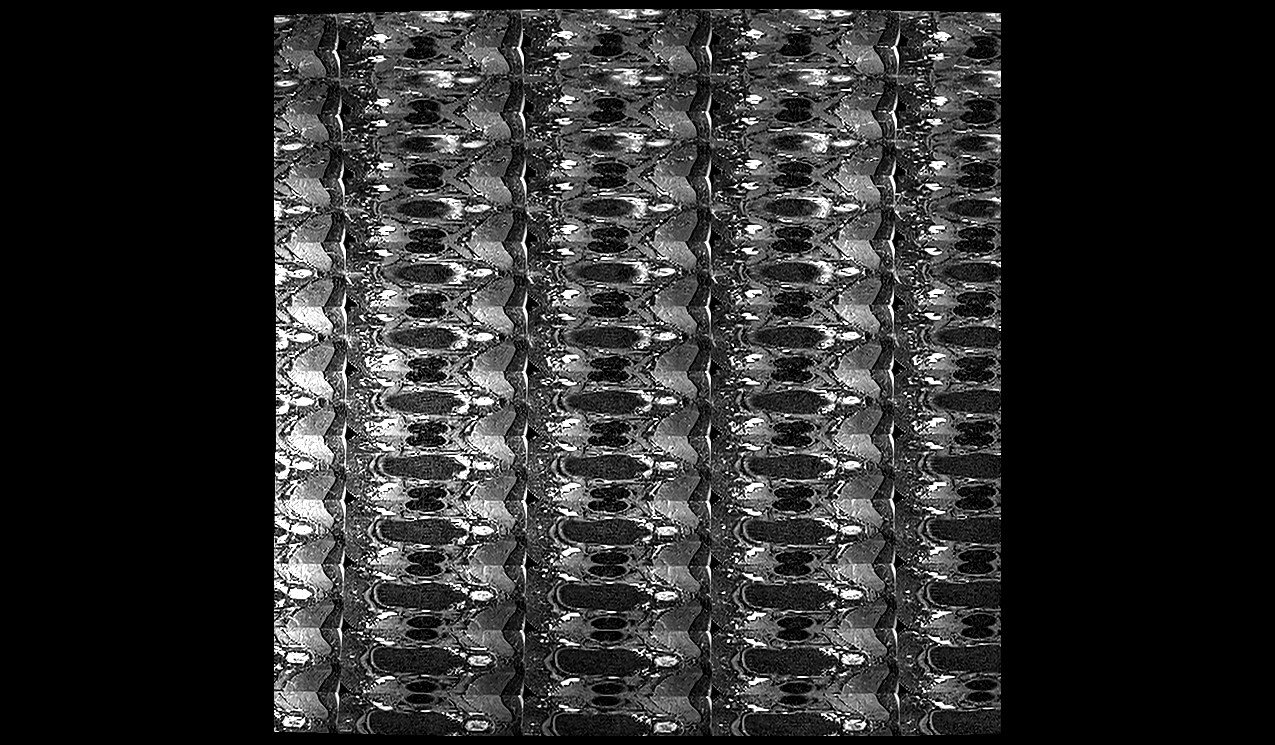
unknown artifacts were fully eliminated by reducing the matrix size to 448x448
References
- Behl, N. (2021). Deep Resolve – Mobilizing the Power of Networks. Global Marketing Manager MRI Systems, Siemens Healthineers, Erlangen, Germany. MAGNETOM Flash (78), 1/2021.
- Lopez Schmidt, I., Haag, N., Shahzadi, I., Frohwein, L. J., Schneider, C., Niehoff, J. H., Kroeger, J. R., Borggrefe, J., Moenninghoff, C. (2023). Diagnostic Image Quality of a Low-Field (0.55T) Knee MRI Protocol Using Deep Learning Image Reconstruction Compared with a Standard (1.5T) Knee MRI Protocol. J Clin Med, 12(5), 1916. doi: 10.3390/jcm12051916.
